Heat and Drought Stress Impact on Phenology, Grain Yield, and Nutritional Quality of Lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus)
- PMID: 33330596
- PMCID: PMC7719779
- DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2020.596307
Heat and Drought Stress Impact on Phenology, Grain Yield, and Nutritional Quality of Lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus)
Abstract
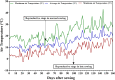
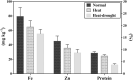
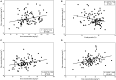
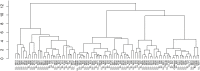
Lentil (Lens culinaris Medikus) is a protein-rich cool-season food legume with an excellent source of protein, prebiotic carbohydrates, minerals, and vitamins. With climate change, heat, and drought stresses have become more frequent and intense in lentil growing areas with a strong influence on phenology, grain yield, and nutritional quality. This study aimed to assess the impact of heat and drought stresses on phenology, grain yield, and nutritional quality of lentil. For this purpose, 100 lentil genotypes from the global collection were evaluated under normal, heat, and combined heat-drought conditions. Analysis of variance revealed significant differences (p < 0.001) among lentil genotypes for phenological traits, yield components, and grain quality traits. Under no stress conditions, mineral concentrations among lentil genotypes varied from 48 to 109 mg kg-1 for iron (Fe) and from 31 to 65 mg kg-1 for zinc (Zn), while crude protein content ranged from 22.5 to 32.0%. Iron, zinc, and crude protein content were significantly reduced under stress conditions, and the effect of combined heat-drought stress was more severe than heat stress alone. A significant positive correlation was observed between iron and zinc concentrations under both no stress and stress conditions. Based on grain yield, crude protein, and iron and zinc concentrations, lentil genotypes were grouped into three clusters following the hierarchical cluster analysis. Promising lentil genotypes with high micronutrient contents, crude protein, and grain yield with the least effect of heat and drought stress were identified as the potential donors for biofortification in the lentil breeding program.
Keywords: biofortification; combined heat-drought; crude protein; grain yield; heat; iron and zinc; lentil; malnutrition.
Copyright © 2020 Choukri, Hejjaoui, El-Baouchi, El haddad, Smouni, Maalouf, Thavarajah and Kumar.
Figures

References
-
- Stevens GA, Finucane MM, De-Regil LM, Paciorek CJ, Flaxman SR, Branca F, et al. Global, regional, and national trends in haemoglobin concentration and prevalence of total and severe anaemia in children and pregnant and non-pregnant women for 1995-2011: a systematic analysis of population-representative data. Lancet Global Health. (2013) 1:e16–e25. 10.1016/S2214-109X(13)70001-9 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

