Fast Deisotoping Algorithm and Its Implementation in the MSFragger Search Engine
- PMID: 33332123
- PMCID: PMC8864561
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00544
Fast Deisotoping Algorithm and Its Implementation in the MSFragger Search Engine
Abstract
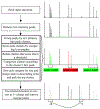
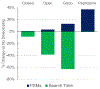
Deisotoping, or the process of removing peaks in a mass spectrum resulting from the incorporation of naturally occurring heavy isotopes, has long been used to reduce complexity and improve the effectiveness of spectral annotation methods in proteomics. We have previously described MSFragger, an ultrafast search engine for proteomics, that did not utilize deisotoping in processing input spectra. Here, we present a new, high-speed parallelized deisotoping algorithm, based on elements of several existing methods, that we have incorporated into the MSFragger search engine. Applying deisotoping with MSFragger reveals substantial improvements to database search speed and performance, particularly for complex methods like open or nonspecific searches. Finally, we evaluate our deisotoping method on data from several instrument types and vendors, revealing a wide range in performance and offering an updated perspective on deisotoping in the modern proteomics environment.
Keywords: MSFragger; deisotoping; nonspecific search; open search; preprocessing; proteomics; spectrum processing.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests Statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Solntsev SK; Shortreed MR; Frey BL; Smith LM, Enhanced Global Post-translational Modification Discovery with MetaMorpheus. Journal of Proteome Research 2018, 17 (5), 1844–1851. - PubMed
-
- Chi H; Liu C; Yang H; Zeng WF; Wu L; Zhou WJ; Wang RM; Niu XN; Ding YH; Zhang Y; Wang ZW; Chen ZL; Sun RX; Liu T; Tan GM; Dong MQ; Xu P; Zhang PH; He SM, Comprehensive identification of peptides in tandem mass spectra using an efficient open search engine. Nature Biotechnology 2018, 36 (11), 1059–1066. - PubMed
-
- Peng J; Zhang H; Niu H; Wu R. a., Peptidomic analyses: The progress in enrichment and identification of endogenous peptides. TrAC 2020, 125, 115835–115835.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

