Engineering a Chemically Defined Hydrogel Bioink for Direct Bioprinting of Microvasculature
- PMID: 33332959
- PMCID: PMC7870577
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00947
Engineering a Chemically Defined Hydrogel Bioink for Direct Bioprinting of Microvasculature
Abstract
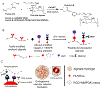
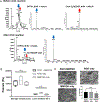
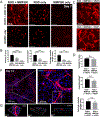
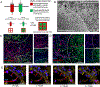
Vascularizing printed tissues is a critical challenge in bioprinting. While protein-based hydrogel bioinks have been successfully used to bioprint microvasculature, their compositions are ill-defined and subject to batch variation. Few studies have focused on engineering proangiogenic bioinks with defined properties to direct endogenous microvascular network formation after printing. Here, a peptide-functionalized alginate hydrogel bioink with defined mechanical, rheological, and biochemical properties is developed for direct bioprinting of microvascularized tissues. An integrin-binding peptide (RGD) and a vascular endothelial growth factor-mimetic peptide with a protease-sensitive linker are conjugated onto a biodegradable alginate to synergistically promote vascular morphogenesis and capillary-scale endothelial tube formation. Partial ionic crosslinking before printing converts the otherwise unprintable hydrogel into a viscoelastic bioink with excellent printability and cytocompatibility. We use the bioink to fabricate a compartmentalized vascularized tissue construct, wherein we observe pericyte-endothelial cell colocalization and angiogenic sprouting across a tissue interface, accompanied by deposition of fibronectin and collagen in vascular and tissue components, respectively. This study provides a tunable and translational "off-the-shelf" hydrogel bioink with defined composition for vascularized bioprinting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Datta P; Ayan B; Ozbolat IT, Bioprinting for vascular and vascularized tissue biofabrication. Acta Biomater. 2017, 51, 1–20. - PubMed
-
- Ozbolat IT, Bioprinting scale-up tissue and organ constructs for transplantation. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, (7), 395–400. - PubMed
-
- Murphy SV; Atala A, 3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat. Biotechnol 2014, 32, (8), 773–85. - PubMed
-
- Segal SS, Regulation of blood flow in the microcirculation. Microcirculation 2005, 12, (1), 33–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

