RNA-Mediated Feedback Control of Transcriptional Condensates
- PMID: 33333019
- PMCID: PMC8128340
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.030
RNA-Mediated Feedback Control of Transcriptional Condensates
Abstract
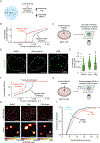
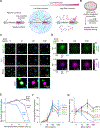
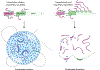
Regulation of biological processes typically incorporates mechanisms that initiate and terminate the process and, where understood, these mechanisms often involve feedback control. Regulation of transcription is a fundamental cellular process where the mechanisms involved in initiation have been studied extensively, but those involved in arresting the process are poorly understood. Modeling of the potential roles of RNA in transcriptional control suggested a non-equilibrium feedback control mechanism where low levels of RNA promote condensates formed by electrostatic interactions whereas relatively high levels promote dissolution of these condensates. Evidence from in vitro and in vivo experiments support a model where RNAs produced during early steps in transcription initiation stimulate condensate formation, whereas the burst of RNAs produced during elongation stimulate condensate dissolution. We propose that transcriptional regulation incorporates a feedback mechanism whereby transcribed RNAs initially stimulate but then ultimately arrest the process.
Keywords: RNA; complex coacervates; enhancer; feedback; mediator; non-equilibrium; noncoding RNA; phase separation; transcription; transcriptional condensates.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests R.A.Y. is a founder and shareholder of Syros Pharmaceuticals, Camp4 Therapeutics, Omega Therapeutics, and Dewpoint Therapeutics. T.I.L. is a shareholder of Syros Pharmaceuticals and a consultant to Camp4 Therapeutics. A.K.C. and P.A.S. are shareholders and consultants to Dewpoint Therapeutics. A.K.C. is a SAB member of Omega Therapeutics. The Whitehead Institute has filed a patent application based on this study.
Figures
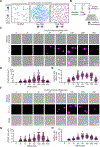
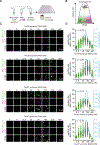
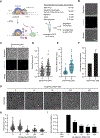
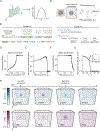
Comment in
-
RNA-mediated (de)condensation.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021 Mar;22(3):164. doi: 10.1038/s41580-021-00340-2. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33526934 No abstract available.
References
-
- Adhikari S, Leaf MA, and Muthukumar M. (2018). Polyelectrolyte complex coacervation by electrostatic dipolar interactions. J Chem Phys 149, 163308. - PubMed
-
- Aumiller WM, Pir Cakmak F, Davis BW, and Keating CD (2016). RNA-Based Coacervates as a Model for Membraneless Organelles: Formation, Properties, and Interfacial Liposome Assembly. Langmuir 32, 10042–10053. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

