Generation of Functional Human 3D Cortico-Motor Assembloids
- PMID: 33333020
- PMCID: PMC8711252
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.017
Generation of Functional Human 3D Cortico-Motor Assembloids
Abstract
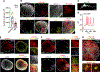
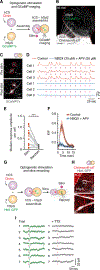
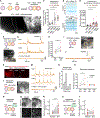
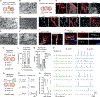
Neurons in the cerebral cortex connect through descending pathways to hindbrain and spinal cord to activate muscle and generate movement. Although components of this pathway have been previously generated and studied in vitro, the assembly of this multi-synaptic circuit has not yet been achieved with human cells. Here, we derive organoids resembling the cerebral cortex or the hindbrain/spinal cord and assemble them with human skeletal muscle spheroids to generate 3D cortico-motor assembloids. Using rabies tracing, calcium imaging, and patch-clamp recordings, we show that corticofugal neurons project and connect with spinal spheroids, while spinal-derived motor neurons connect with muscle. Glutamate uncaging or optogenetic stimulation of cortical spheroids triggers robust contraction of 3D muscle, and assembloids are morphologically and functionally intact for up to 10 weeks post-fusion. Together, this system highlights the remarkable self-assembly capacity of 3D cultures to form functional circuits that could be used to understand development and disease.
Keywords: assembloids; cerebral cortex; connectivity; corticospinal; human pluripotent stem cells; neuromuscular; optogenetics; organoids; rabies tracing; spinal cord.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests Stanford University has filed a provisional patent application that covers the generation and assembly of region-specific cortico-spinal-muscle spheroids. H.C.F. and E.M.W. were employees of BD Genomics during this study.
Figures



Comment in
-
Assembling organs in vitro.Nat Methods. 2021 Feb;18(2):119. doi: 10.1038/s41592-021-01068-9. Nat Methods. 2021. PMID: 33542506 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

