Gene expression profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infections reveal distinct primary lung cell and systemic immune infection responses that identify pathways relevant in COVID-19 disease
- PMID: 33333559
- PMCID: PMC7799202
- DOI: 10.1093/bib/bbaa376
Gene expression profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infections reveal distinct primary lung cell and systemic immune infection responses that identify pathways relevant in COVID-19 disease
Abstract
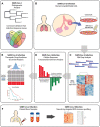
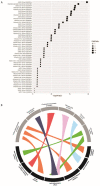
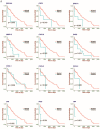
To identify key gene expression pathways altered with infection of the novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2, we performed the largest comparative genomic and transcriptomic analysis to date. We compared the novel pandemic coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 with SARS-CoV and MERS-CoV, as well as influenza A strains H1N1, H3N2 and H5N1. Phylogenetic analysis confirms that SARS-CoV-2 is closely related to SARS-CoV at the level of the viral genome. RNAseq analyses demonstrate that human lung epithelial cell responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection are distinct. Extensive Gene Expression Omnibus literature screening and drug predictive analyses show that SARS-CoV-2 infection response pathways are closely related to those of SARS-CoV and respiratory syncytial virus infections. We validated SARS-CoV-2 infection response genes as disease-associated using Kaplan-Meier survival estimates in lung disease patient data. We also analysed COVID-19 patient peripheral blood samples, which identified signalling pathway concordance between the primary lung cell and blood cell infection responses.
Keywords: COVID-19; MERS-CoV; RNAseq; SARS-CoV; SARS-CoV-2; coronaviruses; transcriptomics.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Center JHCR. John Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center.
-
- Heller N. Primary human airway epithelial cell transcriptome response to a wild type Mers-CoV (icMERS-CoV EMC2012). Gene Expression Omnibus, 2017.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

