The Role of Astrocytes in the Modulation ofK+-Cl--Cotransporter-2 Function
- PMID: 33333849
- PMCID: PMC7765297
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21249539
The Role of Astrocytes in the Modulation ofK+-Cl--Cotransporter-2 Function
Abstract
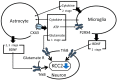
Neuropathic pain is characterized by spontaneous pain, pain sensations, and tactile allodynia. The pain sensory system normally functions under a fine balance between excitation and inhibition. Neuropathic pain arises when this balance is lost for some reason. In past reports, various mechanisms of neuropathic pain development have been reported, one of which is the downregulation of K+-Cl--cotransporter-2 (KCC2) expression. In fact, various neuropathic pain models indicate a decrease in KCC2 expression. This decrease in KCC2 expression is often due to a brain-derived neurotrophic factor that is released from microglia. However, a similar reaction has been reported in astrocytes, and it is unclear whether astrocytes or microglia are more important. This review discusses the hypothesis that astrocytes have a crucial influence on the alteration of KCC2 expression.
Keywords: K+-Cl−-cotransporter-2; astrocyte; brain-derived neurotrophic factor; neuropathic pain; tropomyosin receptor kinase B.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ouyang B., Chen D., Hou X., Wang T., Wang J., Zou W., Song Z., Huang C., Guo Q., Weng Y. Normalizing HDAC2 levels in the spinal cord alleviates thermal and mechanical hyperalgesia after peripheral nerve injury and promotes GAD65 and KCC2 expression. Front. Neurosci. 2019;13:346. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2019.00346. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous