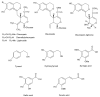
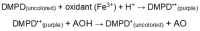Microbiological and Antioxidant Activity of Phenolic Compounds in Olive Leaf Extract
- PMID: 33334001
- PMCID: PMC7765412
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25245946
Microbiological and Antioxidant Activity of Phenolic Compounds in Olive Leaf Extract
Abstract
According to many reports, phenolic compounds isolated from olive leaves have very good biological activities, especially antimicrobial. Presently, the resistance of microorganisms to antibiotics is greater than ever. Therefore, there are numerous recent papers about alternative solutions for inhibiting their influence on human health. Olive leaf is studied as an important source of antimicrobials with low cost and used in medicine. Numerous publications on involving green technologies for isolation of active compounds from olive leaves have appeared over the past few decades. The present review reports on current knowledge of the most isolated phenolic compounds from olive leaf extract as well as methods for their isolation and characterization. This paper uses recent research findings with a wide range of study models to describe the antimicrobial potential of phenolic compounds. It also describes the vast range of information about methods for determination of antimicrobial potential focusing on effects on different microbes. Additionally, it serves to highlight the role of olive leaf extract as an antioxidants and presents methods for determination of antioxidant potential. Furthermore, it provides an overview of presence of enzymes. The significance of olive leaves as industrial and agricultural waste is emphasized by means of explaining their availability, therapeutic and nutritional effects, and research conducted on this field.
Keywords: antimicrobial activity; antioxidant activity; enzymatic activity; olive leaf extract; phenolic compounds; supercritical fluid extraction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of individual and combined phenolics in Olea europaea leaf extract.Bioresour Technol. 2010 May;101(10):3751-4. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.12.052. Epub 2010 Jan 27. Bioresour Technol. 2010. PMID: 20106659
-
Bioavailability of Bioactive Molecules from Olive Leaf Extracts and its Functional Value.Phytother Res. 2016 Jul;30(7):1172-9. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5625. Epub 2016 May 3. Phytother Res. 2016. PMID: 27137173
-
Effects of Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and Solvent on the Phenolic Profile, Bacterial Growth, and Anti-Inflammatory/Antioxidant Activities of Mediterranean Olive and Fig Leaves Extracts.Molecules. 2020 Apr 9;25(7):1718. doi: 10.3390/molecules25071718. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 32283592 Free PMC article.
-
Olive Leaves as a Source of Anticancer Compounds: In Vitro Evidence and Mechanisms.Molecules. 2024 Sep 7;29(17):4249. doi: 10.3390/molecules29174249. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39275097 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Olive tree (Olea europaea L.) leaf as a waste by-product of table olive and olive oil industry: a review.J Sci Food Agric. 2018 Mar;98(4):1271-1279. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8619. Epub 2017 Sep 21. J Sci Food Agric. 2018. PMID: 28799642 Review.
Cited by
-
Simultaneous High-Performance Recovery and Extended Acid-Catalyzed Hydrolysis of Oleuropein and Flavonoid Glycosides of Olive (Olea europaea) Leaves: Hydrothermal versus Ethanol Organosolv Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 17;25(14):7820. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147820. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063062 Free PMC article.
-
Pomegranate Peel and Olive Leaf Extracts to Optimize the Preservation of Fresh Meat: Natural Food Additives to Extend Shelf-Life.Microorganisms. 2024 Jun 27;12(7):1303. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12071303. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39065075 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of a Chitosan Coating Enriched with an Olive Leaf Extract on the Characteristics of Pork Burgers.Foods. 2023 Oct 12;12(20):3757. doi: 10.3390/foods12203757. Foods. 2023. PMID: 37893650 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Study of the Antibacterial Activity of Bioactive Juice and Extracts from Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) Peels and Seeds.Plants (Basel). 2021 Jul 28;10(8):1554. doi: 10.3390/plants10081554. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451599 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant Extracts from Greek and Spanish Olive Leaves: Antimicrobial, Anticancer and Antiangiogenic Effects.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jun 27;13(7):774. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070774. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061845 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Dekanski D., Janićijević-Hudomal S., Ristić S., Radonjić N.V., Petronijević N.D., Piperski V., Mitrović D.M. Attenuation of cold restraint stress-induced gastric lesions by an olive leaf extract. Gen. Physiol. Biophys. 2009;28:135–142. - PubMed
-
- What Is Olive Leaf Extract. [(accessed on 18 June 2020)]; Available online: https://www.superpharmacy.com.au/blog/the-many-benefits-of-olive-leaf-ex....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous