Plasmodial Kinase Inhibitors Targeting Malaria: Recent Developments
- PMID: 33334080
- PMCID: PMC7765515
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25245949
Plasmodial Kinase Inhibitors Targeting Malaria: Recent Developments
Abstract
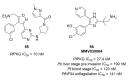
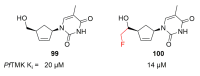
Recent progress in reducing malaria cases and ensuing deaths is threatened by factors like mutations that induce resistance to artemisinin derivatives. Multiple drugs are currently in clinical trials for malaria treatment, including some with novel mechanisms of action. One of these, MMV390048, is a plasmodial kinase inhibitor. This review lists the recently developed molecules which target plasmodial kinases. A systematic review of the literature was performed using CAPLUS and MEDLINE databases from 2005 to 2020. It covers a total of 60 articles and describes about one hundred compounds targeting 22 plasmodial kinases. This work highlights the strong potential of compounds targeting plasmodial kinases for future drug therapies. However, the majority of the Plasmodium kinome remains to be explored.
Keywords: Plasmodium; SAR; kinase inhibitor; malaria; medicinal chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
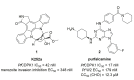
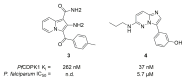
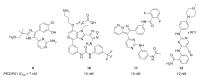
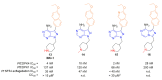
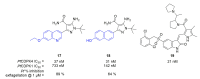
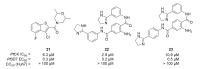
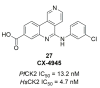
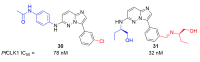
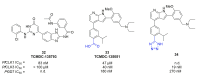
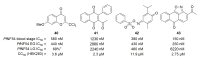
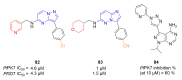
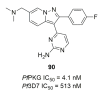
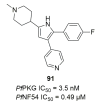
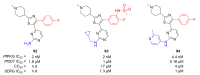
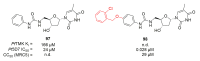
References
-
- World Health Organization World Malaria Report 2019. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2019.
-
- World Health Organization. Global Malaria Programme . Global Technical Strategy for Malaria, 2016–2030. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2015.
-
- Birnbaum J., Scharf S., Schmidt S., Jonscher E., Hoeijmakers W.A.M., Flemming S., Toenhake C.G., Schmitt M., Sabitzki R., Bergmann B., et al. A Kelch13-defined endocytosis pathway mediates artemisinin resistance in malaria parasites. Science. 2020;367:51–59. doi: 10.1126/science.aax4735. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

