Outcome of a single XEN microstent implant for glaucoma patients with different types of glaucoma
- PMID: 33334311
- PMCID: PMC7745382
- DOI: 10.1186/s12886-020-01764-8
Outcome of a single XEN microstent implant for glaucoma patients with different types of glaucoma
Abstract
Background: The aim of this retrospective study was to compare the efficacy and safety profile of a single XEN-microstent in different types of primary and secondary open angle glaucoma.
Methods: A single XEN microstent was implanted in patients with primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), normal-tension glaucoma (NTG), pseudoexfoliation glaucoma (PEX) and secondary glaucoma (Sec.Gl). The intraocular pressure (IOP), the active substances of the applied IOP-lowering drugs, the best corrected visual acuity (BCVA) and the mean deviation (MD) of the perimetry were measured at baseline and at regular follow-ups, scheduled at 2 days and 1, 3, 6 and 12 months after surgery.
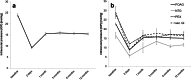
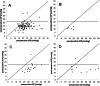
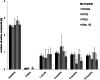
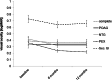
Results: 153 eyes were included in this analysis. 113 eyes were affected by POAG (74%), 5 eyes by NTG (3%), 22 eyes by PEX (14%) and 13 eyes by Sec. Gl (9%). Mean IOP decreased in all treatment groups during the 12 months of follow-up (complete group: 23.9 ± 7.4 to 15.4 ± 5.1 mmHg (p < 0.01); POAG: 22.8 ± 6.5 to 15.1 ± 4.6 mmHg (p < 0.01); NTG: 16.6 ± 3.4 to 11.6 ± 2.2 mmHg (p < 0.05); PEX: 28.0 ± 7.9 to 17.1 ± 6.6 mmHg (p < 0.01); Sec.Gl: 28.9 ± 13.9 to 15.5 ± 6.9 mmHg (p < 0.05)). In the 153 eyes the average number of IOP-lowering drugs applied decreased from 2.6 ± 1.2 to 0.8 ± 1.3 12 months after surgery (p < 0.01). BCVA and mean deviation of automated standard perimetry remained stable in all groups during follow-up.
Conclusion: As in eyes suffering from POAG, IOP and number of IOP-lowering drugs applied can be effectively reduced by XEN implantation in eyes suffering from NTG, PEX and secondary glaucoma while leaving BCVA and visual field unchanged.
Trial registration: Trial was registered at DRKS (registration number: DRKS00020800 , Registered 25.February 2020 - Retrospectively registered).
Keywords: MIGS; Primary open-angle Glaucoma; Trabeculectomy; XEN.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Four-year results of a minimally invasive transscleral glaucoma gel stent implantation in a prospective multi-centre study.Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019 Jul;47(5):581-587. doi: 10.1111/ceo.13463. Epub 2019 Feb 3. Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 30578661 Free PMC article.
-
Comparing the efficacy of trabeculectomy and XEN gel microstent implantation for the treatment of primary open-angle glaucoma: a retrospective monocentric comparative cohort study.Sci Rep. 2020 Nov 9;10(1):19337. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-76551-y. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 33168873 Free PMC article.
-
Two-year outcomes of minimally invasive XEN Gel Stent implantation in primary open-angle and pseudoexfoliation glaucoma.Acta Ophthalmol. 2021 Jun;99(4):369-375. doi: 10.1111/aos.14627. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Acta Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 32996702 Free PMC article.
-
[XEN® Gel Stent for management of chronic open angle glaucoma: A review of the literature (French translation of the article)].J Fr Ophtalmol. 2019 Apr;42(4):391-403. doi: 10.1016/j.jfo.2018.10.005. Epub 2019 Mar 14. J Fr Ophtalmol. 2019. PMID: 30879831 Review. French.
-
Ab interno trabecular bypass surgery with Schlemm´s canal microstent (Hydrus) for open angle glaucoma.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 9;3(3):CD012740. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012740.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32147807 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of XEN gel stent implantation combined with mitomycin C injection in the treatment of open-angle glaucoma: a meta-analysis.Int Ophthalmol. 2024 Nov 5;44(1):410. doi: 10.1007/s10792-024-03306-3. Int Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39499348 Free PMC article.
-
Two Year Functional and Structural Changes-A Comparison between Trabeculectomy and XEN Microstent Implantation Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 1;11(19):5840. doi: 10.3390/jcm11195840. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36233707 Free PMC article.
-
The Outcomes of XEN Gel Stent Implantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Feb 4;9:804847. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.804847. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35186992 Free PMC article.
-
XEN®-45 implantation for refractory uveitic glaucoma.Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024 Mar;262(3):937-948. doi: 10.1007/s00417-023-06254-3. Epub 2023 Oct 19. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 37855957 Free PMC article.
-
Results of XEN45 Gel Stent Implantation in the Treatment of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Using 5, 10 or 20 μg Mitomycin C: A Pilot Study.J Ophthalmol. 2024 Oct 26;2024:3895054. doi: 10.1155/2024/3895054. eCollection 2024. J Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 39492955 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

