Characterization of neonates born to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection: Review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33334687
- PMCID: PMC7585378
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2020.10.001
Characterization of neonates born to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection: Review and meta-analysis
Abstract
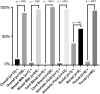
Characterization of neonates born to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection has been partially carried out. There has been no systematic review providing a holistic neonatal presentation including possible vertical transmission. A systematic literature search was performed using PubMed, Google Scholar and Web of Science up to June, 6 2020. Studies on neonates born to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection were included. A binary random effect model was used for prevalence and 95% confidence interval. 32 studies involving 261 neonates were included in meta-analysis. Most neonates born to infected mothers did not show any clinical abnormalities (80.4%). Clinical features were dyspnea in 11 (42.3%) and fever in 9 newborns (19.1%). Of 261 neonates, 120 neonates were tested for infection, of whom 12 (10.0%) tested positive. Swabs from placenta, cord blood and vaginal secretion were negative. Neonates are mostly non affected by the mother's SARS-CoV-2 infection. The risk of vertical transmission is low.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; infant; neonate; newborn.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier B.V.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest All authors claim to have no conflicts of interest in connection with the subject of this publication.
Figures
Comment in
-
Comment on "Characterization of neonates born to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection: Review and meta-analysis".Pediatr Neonatol. 2021 Nov;62(6):691-692. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2021.08.003. Epub 2021 Aug 30. Pediatr Neonatol. 2021. PMID: 34503940 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Response to: Characterization of neonates born to mothers with SARS-CoV-2 infection: Review and meta-analysis.Pediatr Neonatol. 2021 Nov;62(6):693. doi: 10.1016/j.pedneo.2021.08.007. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Pediatr Neonatol. 2021. PMID: 34518126 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organisation . World Health Organization; 2020. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic 2020.https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019 Available at. Accessed May 27, 2020.
-
- Johns Hopkins University . Johns Hopkins University; 2020. COVID-19 dashboard by the center for Systems science and engineering (CSSE) at Johns Hopkins university (JHU)https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html Available at. Accessed May 27, 2020.
Further reading
-
- Kalafat E., Yaprak E., Cinar G., Varli B., Ozisik S., Uzun C. Lung ultrasound and computed tomographic findings in pregnant woman with COVID-19. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2020;55:835–837. - PubMed
-
- Liu D., Li L., Wu X., Zheng D., Wang J., Yang L. Pregnancy and perinatal outcomes of women with coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pneumonia: a preliminary analysis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020;215:127–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

