Secukinumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis and axial manifestations: results from the double-blind, randomised, phase 3 MAXIMISE trial
- PMID: 33334727
- PMCID: PMC8053347
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-218808
Secukinumab in patients with psoriatic arthritis and axial manifestations: results from the double-blind, randomised, phase 3 MAXIMISE trial
Abstract
Objectives: MAXIMISE (Managing AXIal Manifestations in psorIatic arthritis with SEcukinumab) trial was designed to evaluate the efficacy of secukinumab in the management of axial manifestations of psoriatic arthritis (PsA).
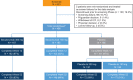
Methods: This phase 3b, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multi-centre 52-week trial included patients (≥18 years) diagnosed with PsA and classified by ClASsification criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis (CASPAR) criteria, with spinal pain Visual Analogue Score ≥40/100 and Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) score ≥4 despite use of at least two non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Patients were randomised (1:1:1) to secukinumab 300 mg, secukinumab 150 mg or placebo weekly for 4 weeks and every 4 weeks thereafter. At week 12, placebo patients were re-randomised to secukinumab 300/150 mg. Primary endpoint was ASAS20 (Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society) response with secukinumab 300 mg at week 12.
Results: Patients were randomly assigned; 167 to secukinumab 300 mg, 165 to secukinumab 150 mg and 166 to placebo. Secukinumab 300 mg and 150 mg significantly improved ASAS20 response versus placebo at week 12 (63% and 66% vs 31% placebo). The OR (95% CI) comparing secukinumab 300 mg and 150 mg versus placebo, using a logistic regression model after multiple imputation, was 3.8 (2.4 and 6.1) and 4.4 (2.7 and 7.0; p<0.0001).
Conclusions: Secukinumab 300 mg and 150 mg provided significant improvement in signs and symptoms of axial disease compared with placebo in patients with PsA and axial manifestations with inadequate response to NSAIDs.
Trial registration number: NCT02721966.
Keywords: antirheumatic agents; arthritis; biological therapy; low back pain; psoriatic; tumor necrosis factor inhibitors.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2021. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: XB: Grant/research support from: AbbVie, and Novartis, Consultant for: AbbVie, BMS, Celgene, Chugai, Galapagos, Gilead, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB; Speakers bureau: AbbVie, BMS, Celgene, Chugai, MSD, Novartis, Pfizer, and UCB. LG: Research grants: Amgen, Lilly, Janssen, Pfizer, Sandoz, Sanofi, and Galapagos; consulting fees: AbbVie, Amgen, BMS, Biogen, Celgene, Gilead, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Samsung Bioepis, Sanofi-Aventis and UCB. EP: Employee of Novartis with Novartis stock. SJ: Research support/speaker: AbbVie, Pfizer, Roche, Novartis, MSD, Sandoz, Lilly, Egis, UCB and Celgene. AM-V: None declared. SD: Consultant for AbbVie, Biogen, BMS, Celgene, Lilly, MSD, Novartis and UCB; Speakers bureau: AbbVie, BMS and Celgene, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer and Sanofi. BS: Employee of Novartis. MR: Employee of Novartis with Novartis stock. KN: Employee of Novartis. CP: Employee of Novartis with Novartis stock. LCC: Grant/research support: AbbVie, Janssen, Lilly, Novartis and Pfizer; Consultant for: AbbVie, Amgen, Biogen, Celgene, Pfizer, UCB, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novartis, Lilly, Janssen, Sun Pharma, Prothena and Gilead.
Figures


References
-
- Baraliakos X, Coates LC, Braun J. The involvement of the spine in psoriatic arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 2015;33:S31–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

