A Randomized Clinical Trial Assessing Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Use With Standardized Education With or Without a Family Behavioral Intervention Compared With Fingerstick Blood Glucose Monitoring in Very Young Children With Type 1 Diabetes
- PMID: 33334807
- PMCID: PMC9162100
- DOI: 10.2337/dc20-1060
A Randomized Clinical Trial Assessing Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) Use With Standardized Education With or Without a Family Behavioral Intervention Compared With Fingerstick Blood Glucose Monitoring in Very Young Children With Type 1 Diabetes
Abstract
Objective: This study evaluated the effects of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) combined with family behavioral intervention (CGM+FBI) and CGM alone (Standard-CGM) on glycemic outcomes and parental quality of life compared with blood glucose monitoring (BGM) in children ages 2 to <8 years with type 1 diabetes.
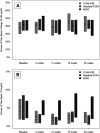
Research design and methods: This was a multicenter (N = 14), 6-month, randomized controlled trial including 143 youth 2 to <8 years of age with type 1 diabetes. Primary analysis included treatment group comparisons of percent time in range (TIR) (70-180 mg/dL) across follow-up visits.
Results: Approximately 90% of participants in the CGM groups used CGM ≥6 days/week at 6 months. Between-group TIR comparisons showed no significant changes: CGM+FBI vs. BGM 3.2% (95% CI -0.5, 7.0), Standard-CGM vs. BGM 0.5% (-2.6 to 3.6), CGM+FBI vs. Standard-CGM 2.7% (-0.6, 6.1). Mean time with glucose level <70 mg/dL was reduced from baseline to follow-up in the CGM+FBI (from 5.2% to 2.6%) and Standard-CGM (5.8% to 2.5%) groups, compared with 5.4% to 5.8% with BGM (CGM+FBI vs. BGM, P < 0.001, and Standard-CGM vs. BGM, P < 0.001). No severe hypoglycemic events occurred in the CGM+FBI group, one occurred in the Standard-CGM group, and five occurred in the BGM group. CGM+FBI parents reported greater reductions in diabetes burden and fear of hypoglycemia compared with Standard-CGM (P = 0.008 and 0.04) and BGM (P = 0.02 and 0.002).
Conclusions: CGM used consistently over a 6-month period in young children with type 1 diabetes did not improve TIR but did significantly reduce time in hypoglycemia. The FBI benefited parental well-being.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02912728.
© 2020 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Mauras N, Beck R, Xing D, et al.; Diabetes Research in Children Network (DirecNet) Study Group . A randomized clinical trial to assess the efficacy and safety of real-time continuous glucose monitoring in the management of type 1 diabetes in young children aged 4 to <10 years. Diabetes Care 2012;35:204–210 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sundberg F, Forsander G. Detection and treatment efficacy of hypoglycemic events in the everyday life of children younger than 7 yr. Pediatr Diabetes 2014;15:34–40 - PubMed
-
- Rovet JF, Ehrlich RM. The effect of hypoglycemic seizures on cognitive function in children with diabetes: a 7-year prospective study. J Pediatr 1999;134:503–506 - PubMed
-
- Rovet JF, Ehrlich RM, Hoppe M. Specific intellectual deficits in children with early onset diabetes mellitus. Child Dev 1988;59:226–234 - PubMed
-
- Ryan CM. Searching for the origin of brain dysfunction in diabetic children: going back to the beginning. Pediatr Diabetes 2008;9:527–530 - PubMed