A Novel Surgical Technique to Assure Donor and Recipient Safety: Pyloric to Segment 4 Arterial Reconstruction
- PMID: 33335979
- PMCID: PMC7738044
- DOI: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001095
A Novel Surgical Technique to Assure Donor and Recipient Safety: Pyloric to Segment 4 Arterial Reconstruction
Abstract
Background: Strategies to extend the pool of organs include and promote the use of segmental liver grafts. While performing a living donor left lateral segment (LLS) liver transplant and in split procedures, the hepatic artery´s division becomes critical when a dominant segment 4 artery (S4A) emerges from the left hepatic artery (LHA). We aim to describe a novel technique that consists of performing microsurgical reconstruction from the pyloric artery (PA) to S4A.
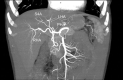
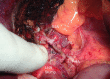
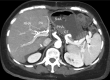
Case reports: A 45-y-old living donor was evaluated to use his LLS as a graft for a pediatric recipient. During the procedure, a dominant S4A born from the LHA was dissected. To obtain an appropriate LHA length and diameter for the recipient, it was necessary to transect it. An extended right lobe split graft was used in a 61-y-old patient. The S4A born from LHA had to be sectioned during the split procedure. In both cases, segment 4 remained incompletely perfused. The PA was dissected with enough length to be rotated, to perform a microsurgical anastomosis to the S4A, recovering parenchyma's color and Doppler signal while vascular permeability was demonstrated using CT scan. There was no biliary or cut surface complication.
Conclusions: PA to S4A reconstruction is a simple and novel technique that can be used for LLS and extended right lobe split graft and might contribute to increase donor selection and reduce living donor and recipient S4A-related complications.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Transplantation Direct. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no funding or conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Strasberg S, Belghiti J, Clavien P-A, et al. The Brisbane 2000 terminology of liver anatomy and resections. HPB (Oxford). 2000; 2:333–9.
-
- Sepulveda A, Scatton O, Tranchart H, et al. Split liver transplantation using extended right grafts: the natural history of segment 4 and its impact on early postoperative outcomes. Liver Transpl. 2012; 18:413–422. - PubMed
-
- Halac E, Dip M, Quiñonez E, et al. Split liver transplantation: report of right and left graft outcomes from a multicenter Argentinean group. Liver Transpl. 2016; 22:63–70. - PubMed
-
- Renz JF, Yersiz H, Reichert PR, et al. Split-liver transplantation: a review. Am J Transplant. 2003; 3:1323–1335. - PubMed
-
- Chan SC, Lo CM, Liu CL, et al. Tailoring donor hepatectomy per segment 4 venous drainage in right lobe live donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2004; 10:755–762. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

