Sirtuins, brain and cognition: A review of resveratrol effects
- PMID: 33336103
- PMCID: PMC7733131
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ibror.2020.06.004
Sirtuins, brain and cognition: A review of resveratrol effects
Abstract
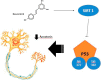
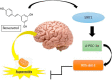
Sirtuins (SIRTs) are a protein family with high preservation degree among evolutionary scale. SIRTs are histone deacetylases regulatory enzymes of genetic material deeply involved in numerous physiological tasks including metabolism, brain function and aging. Mammals sirtuins comprise seven enzymatic components (SIRT1-SIRT7). The highest studied sirtuin is SIRT1, which plays an essential position in the prevention and evolution of neuro-disorders. Resveratrol (3,5,4-trihydroxystylbene) (RSV) is a polyphenol, which belongs to a family compounds identified as stilbenes, predominantly concentrated in grapes and red wine. RSV is the must studied Sirtuin activator and is used as food supplementary compound. Resveratrol exhibits strong antioxidant activity, reducing free radicals, diminishing quinone-reductase-2 activity and exerting positive regulation of several endogenous enzymes. Resveratrol is also able to inhibit pro-inflammatory factors, reducing the stimulation of the nuclear factor kB (NF-kB) and the release of endogenous cytokines. Resveratrol treatment can modulate multiple signaling pathway effectors related to programmed cell death, cell survival, and synaptic plasticity. In this context, the present review looks over news and the role of Sirtuins activation and resveratrol effects on modulating target genes, cognition and neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Central nervous system; Phytochemistry family; Polyphenol; Sirt; Wine.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Alcendor R.R., Gao S., Zhai P., Zablocki D., Holle E., Yu X. Sirt1 regulates aging and resistance to oxidative stress in the heart. Circ. Res. 2007;100(10):1512–1521. - PubMed
-
- Almeida S., Alves M.G., Sousa M., Oliveira P.F., Silva B.M. Are polyphenols strong dietary agents against neurotoxicity and neurodegeneration? Neurotox. Res. 2016;30(3):345–366. - PubMed
-
- Anastacio J.R., Netto C.A., Castro C.C., Sanches E.F., Ferreira D.C., Noschang C. Resveratrol treatment has neuroprotective effects and prevents cognitive impairment after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Neurol. Res. 2014;36(7):627–633. - PubMed
-
- Andrade J.M.O., Barcala-Jorge A.S., Batista-Jorge G.C., Paraiso A.F., Freitas K.M., Lelis D.F. Effect of resveratrol on expression of genes involved thermogenesis in mice and humans. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019;112:108634. - PubMed
-
- Apostolo J., Holland C., O’Connell M.D., Feeney J., Tabares-Seisdedos R., Tadros G. Mild cognitive decline. A position statement of the Cognitive Decline Group of the European Innovation Partnership for Active and Healthy Ageing (EIPAHA) Maturitas. 2016;83:83–93. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

