Antagonism of Type I Interferon by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
- PMID: 33337934
- PMCID: PMC7757701
- DOI: 10.1089/jir.2020.0214
Antagonism of Type I Interferon by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Abstract
The coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), warranting urgent study of the molecular mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 infection and host immune response. Type I interferon (IFN-I) is a key component of host innate immune system responsible for eliminating the virus at the early stage of infection. In contrast, SARS-CoV-2 has evolved multiple strategies to evade innate immune response to facilitate viral replication, transmission, and pathogenesis. This review summarizes the recent progresses on SARS-CoV-2 proteins that antagonize host IFN-I production and/or signaling. These progresses have provided knowledge for new vaccine and antiviral development to prevent and control COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; immune evasion; interferon.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
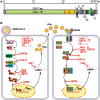
References
-
- Assiri A, Al-Tawfiq JA, Al-Rabeeah AA, Al-Rabiah FA, Al-Hajjar S, Al-Barrak A, Flemban H, Al-Nassir WN, Balkhy HH, Al-Hakeem RF, et al. 2013. Epidemiological, demographic, and clinical characteristics of 47 cases of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus disease from Saudi Arabia: a descriptive study. Lancet Infect Dis 13(9):752–761 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Balachandran S, Roberts PC, Brown LE, Truong H, Pattnaik AK, Archer DR, Barber GN. 2000. Essential role for the dsRNA-dependent protein kinase PKR in innate immunity to viral infection. Immunity 13(1):129–141 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
