Environmental fluctuations and their effects on microbial communities, populations and individuals
- PMID: 33338228
- PMCID: PMC8371271
- DOI: 10.1093/femsre/fuaa068
Environmental fluctuations and their effects on microbial communities, populations and individuals
Abstract
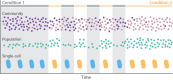
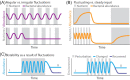
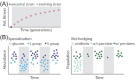
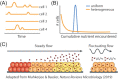
From the homeostasis of human health to the cycling of Earth's elements, microbial activities underlie environmental, medical and industrial processes. These activities occur in chemical and physical landscapes that are highly dynamic and experienced by bacteria as fluctuations. In this review, we first discuss how bacteria can experience both spatial and temporal heterogeneity in their environments as temporal fluctuations of various timescales (seconds to seasons) and types (nutrient, sunlight, fluid flow, etc.). We then focus primarily on nutrient fluctuations to discuss how bacterial communities, populations and single cells respond to environmental fluctuations. Overall, we find that environmental fluctuations are ubiquitous and diverse, and strongly shape microbial behavior, ecology and evolution when compared with environments in which conditions remain constant over time. We hope this review may serve as a guide toward understanding the significance of environmental fluctuations in microbial life, such that their contributions and implications can be better assessed and exploited.
Keywords: changing environments; microbial evolution; microbial physiology; microbial responses; population dynamics; single cell.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of FEMS.
Figures


References
-
- Acar M, Mettetal JT, Van Oudenaarden A. Stochastic switching as a survival strategy in fluctuating environments. Nat Genet. 2008;40:471. - PubMed
-
- Ackermann M. A functional perspective on phenotypic heterogeneity in microorganisms. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2015;13:497–508. - PubMed
-
- Ahmerkamp S, Winter C, Janssen Fet al. The impact of bedform migration on benthic oxygen fluxes. J Geophys Res-Biogeo. 2015;120:2229–42.
-
- Arevalo P, VanInsberghe D, Elsherbini Jet al. A Reverse Ecology Approach Based on a Biological Definition of Microbial Populations. Cell. 2019;178:820–34. - PubMed
-
- Azam F, Malfatti F.. Microbial structuring of marine ecosystems. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2007;5:782–91. - PubMed

