COVID-19 and thrombosis: From bench to bedside
- PMID: 33338635
- PMCID: PMC7836332
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tcm.2020.12.004
COVID-19 and thrombosis: From bench to bedside
Abstract
Coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) is the respiratory viral infection caused by the coronavirus SARS-CoV2 (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2). Despite being a respiratory illness, COVID-19 is found to increase the risk of venous and arterial thromboembolic events. Indeed, the link between COVID-19 and thrombosis is attracting attention from the broad scientific community. In this review we will analyze the current available knowledge of the association between COVID-19 and thrombosis. We will highlight mechanisms at both molecular and cellular levels that may explain this association. In addition, the article will review the antithrombotic properties of agents currently utilized or being studied in COVID-19 management. Finally, we will discuss current professional association guidance on prevention and treatment of thromboembolism associated with COVID-19.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
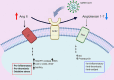
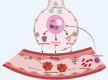
Comment in
-
Editorial commentary: Understanding thrombosis in COVID-19 - A long way to go.Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Apr;31(3):161-162. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2020.12.006. Epub 2020 Dec 28. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 33383172 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Xu X, Chang XN, Pan HX, Su H, Huang B, Yang M, et al. Pathological changes of the spleen in ten patients with coronavirus disease 2019(COVID-19) by postmortem needle autopsy. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi. 2020;49(6):576–582. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

