Toxicological Screening of Four Bioactive Citroflavonoids: In Vitro, In Vivo, and In Silico Approaches
- PMID: 33339310
- PMCID: PMC7766697
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25245959
Toxicological Screening of Four Bioactive Citroflavonoids: In Vitro, In Vivo, and In Silico Approaches
Abstract
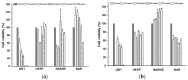
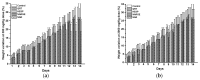
Many studies describe different pharmacological effects of flavonoids on experimental animals and humans. Nevertheless, few ones are confirming the safety of these compounds for therapeutic purposes. This study aimed to investigate the preclinical safety of naringenin, naringin, hesperidin, and quercetin by in vivo, in vitro, and in silico approaches. For this, an MTT-based cytotoxicity assay in VERO and MDCK cell lines was performed. In addition, acute toxicity was evaluated on Wistar rats by OECD Guidelines for the Testing of Chemicals (Test No. 423: Acute Oral Toxicity-Class Method). Furthermore, we used the ACD/Tox Suite to predict toxicological parameters such as hERG channel blockade, CYP450 inhibition, and acute toxicity in animals. The results showed that quercetin was slightly more cytotoxic on cell lines (IC50 of 219.44 ± 7.22 mM and 465.41 ± 7.44 mM, respectively) than the other citroflavonoids. All flavonoids exhibited an LD50 value > 2000 mg/kg, which classifies them as low-risk substances as OECD guidelines established. Similarly, predicted LD50 was LD50 > 300 to 2000 mg/kg for all flavonoids as acute toxicity assay estimated. Data suggests that all these flavonoids did not show significant toxicological effects, and they were classified as low-risk, useful substances for drug development.
Keywords: MTT-based assay; acute oral toxicity; citroflavonoids; low-risk substances; toxicity prediction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hussain K.A., Tarakji B., Panar Kandy B.P., Jhon J., Mathews J., Ramphul V., Divakar D.D. Antimicrobial effects of Citrus sinensis Peel extracts against periodontopathic bacteria: An in vitro study. Rocz. Panstw. Zakl. Hig. 2015;66:173–178. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi G.R., Silva Vasconcelos A.B., Wu D.-T., Li H.-B., Antony P.J., Li H., Geng F., Queiroz Gurgel R., Narain N., Gan R.-Y. Citrus Flavonoids as Promising Phytochemicals Targeting Diabetes and Related Complications: A Systematic Review of In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Nutrients. 2020;12:2907. doi: 10.3390/nu12102907. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

