Late-onset myocardial infarction and autoimmune haemolytic anaemia in a COVID-19 patient without respiratory symptoms, concomitant with a paradoxical increase in inflammatory markers: a case report
- PMID: 33339534
- PMCID: PMC7746982
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-020-02595-3
Late-onset myocardial infarction and autoimmune haemolytic anaemia in a COVID-19 patient without respiratory symptoms, concomitant with a paradoxical increase in inflammatory markers: a case report
Abstract
Background: In December 2019, a new coronavirus (named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, SARS-CoV-2) spread from China, causing a pandemic in a very short time. The main clinical presentation of SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19, coronavirus disease-2019) is pneumonia, but several cardiovascular complications may also occur (e.g., acute coronary syndromes, pulmonary embolism, stroke, arrhythmias, heart failure and cardiogenic shock). Direct or indirect mechanisms induced by SARS-CoV-2 could be implicated in the pathogenesis of these events.
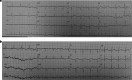
Case presentation: We report herein the third case of COVID-19 autoimmune haemolytic anaemia (AIHA) reported so far, which occurredwithout any other possible explanations in a Caucasian patient. The patient also suffered from ST-elevation myocardial injury.
Conclusions: Both complications occurred quite late after COVID-19 diagnosis and were probably precipitated by systemic inflammation, as indicated by a significant delayed increase in inflammatory markers, including interleukin-6 (IL-6).
Keywords: AIHA; Anaemia; COVID-19; Cardiovascular disease; IL-6; Inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Gautret P, Lagier JC, Parola P, et al. Hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin as a treatment of COVID-19: results of an open-label non-randomized clinical trial [published online ahead of print, 2020 Mar 20] Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2020;2020:105949. doi: 10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105949. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Vademecum for the treatment of people with COVID-19 disease. Edition 2.0, 13 March 2020. Lombardy Section of the Italian Society of Infectious and Tropical Diseases. InfezMed 2020; 28 (2), 143-152 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous