Impact of chronic kidney disease on health-related quality of life in the pediatric population: meta-analysis
- PMID: 33340460
- PMCID: PMC9432262
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jped.2020.10.013
Impact of chronic kidney disease on health-related quality of life in the pediatric population: meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: To meta-analyze health-related quality of life in pediatric patients with chronic kidney disease in comparison to healthy patients according to the dimensions of the PedsQL instrument.
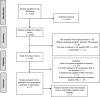
Sources of data: A systematic review was performed with meta-analysis for the mean difference in each of the health-related quality of life dimensions. The authors searched for ten scientific databases including PubMed, Scopus, SciELO, Science Direct, ProQuest, Google Scholar. Reproducibility by the Kappa index was evaluated, and Dersimonian and Laird's tests, RI coefficient, Begg statistic, Forest Plot, and sensitivity analysis were carried out.
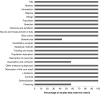
Summary of the findings: 17 investigations were included in the qualitative synthesis and 7 in the quantitative synthesis with a population of 1214 of both healthy and sick pediatric patients with 3-5 chronic kidney disease stages. The health-related quality of life in pediatric chronic kidney disease patients presented lower scores in all the evaluated dimensions: in the physical dimension the difference is of 13.6 points, in the emotional dimension 7.8, in the social dimension 8.2, in the school dimension 20.8, with the total difference being 17.7 points.
Conclusion: The findings of this study show that pediatric patients have lower health-related quality of life in all the evaluated dimensions, with the "school" dimension being the most affected and the "emotional" one the least. In this sense, we suggest monitoring the health-related quality of life of pediatric patients with chronic kidney disease so that interventions can be oriented to strengthen the affected dimensions, including adjustments to daily life and prevention of complications related to the disease.
Keywords: Child; Chronic kidney disease; Pediatric; Quality of life.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Health-related quality of life for pediatric patients with end-stage kidney disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory (PedsQL).Hemodial Int. 2024 Apr;28(2):198-215. doi: 10.1111/hdi.13138. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Hemodial Int. 2024. PMID: 38468403
-
Measuring health-related quality of life in children with ESRD: performance of the generic and ESRD-specific instrument of the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory (PedsQL).Am J Kidney Dis. 2008 Feb;51(2):285-97. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2007.09.021. Am J Kidney Dis. 2008. PMID: 18215706
-
The impact of short stature on health-related quality of life in children with chronic kidney disease.J Pediatr. 2013 Sep;163(3):736-41.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.03.016. Epub 2013 Apr 26. J Pediatr. 2013. PMID: 23628375 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of summer programmes on the outcomes of disadvantaged or 'at risk' young people: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2024 Jun 13;20(2):e1406. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1406. eCollection 2024 Jun. Campbell Syst Rev. 2024. PMID: 38873396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Health-related quality of life of children with mild to moderate chronic kidney disease.Pediatrics. 2010 Feb;125(2):e349-57. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-0085. Epub 2010 Jan 18. Pediatrics. 2010. PMID: 20083528 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Pruritus Features in Children with End-Stage Renal Disease Underwent Dialysis: A Cross-Sectional Study.Int J Pediatr. 2021 Jul 28;2021:9970321. doi: 10.1155/2021/9970321. eCollection 2021. Int J Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 34367296 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-Effectiveness of Intensive Blood Pressure Control in Youth With Chronic Kidney Disease.Hypertension. 2025 Feb;82(2):393-401. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.124.23437. Epub 2024 Dec 5. Hypertension. 2025. PMID: 39633564
-
Common mental health conditions and considerations in pediatric chronic kidney disease.Pediatr Nephrol. 2024 Oct;39(10):2887-2897. doi: 10.1007/s00467-024-06314-8. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Pediatr Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38456918 Review.
-
Symptoms for early diagnosis of chronic kidney disease in children - a machine learning-based score.Eur J Pediatr. 2023 Aug;182(8):3631-3637. doi: 10.1007/s00431-023-05032-x. Epub 2023 May 26. Eur J Pediatr. 2023. PMID: 37233777
-
Pediatric Chronic Kidney Disease: Mind the Gap Between Reality and Expectations.Children (Basel). 2025 May 8;12(5):614. doi: 10.3390/children12050614. Children (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40426793 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ribeiro K.R. Cuidados de enfermagem aos pacientes com insuficiência renal crônica no ambientes hospitalar. Rev Cient Enferm. 2016;6:26–35.
-
- Flores J.C. Chronic Kidney Disease: epidemiology and risk factors. Rev Med Clinc Condes. 2010;21:502–507.
-
- Ministerio de Sanidad Servicios Sociales e Igualdad Dirección General de Salud Pública. Documento Marco sobre Enfermedad Renal Crónica (ERC) dentro de la Estrategia de Abordaje a la Cronicidad en el SNS [Internet]. 2015 [accessed 26 Sept. 2018]. Available from: http://www.senefro.org/modules/noticias/images/enfermedad_renal_cronica_....
-
- García de Vinuesa S. Progression factors for chronic kidney disease. Secondary prevention. Nefrologia. 2008;28:17–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

