Comparison of the characteristics, morbidity, and mortality of COVID-19 and seasonal influenza: a nationwide, population-based retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 33341155
- PMCID: PMC7832247
- DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30527-0
Comparison of the characteristics, morbidity, and mortality of COVID-19 and seasonal influenza: a nationwide, population-based retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: To date, influenza epidemics have been considered suitable for use as a model for the COVID-19 epidemic, given that they are respiratory diseases with similar modes of transmission. However, data directly comparing the two diseases are scarce.
Methods: We did a nationwide retrospective cohort study using the French national administrative database (PMSI), which includes discharge summaries for all hospital admissions in France. All patients hospitalised for COVID-19 from March 1 to April 30, 2020, and all patients hospitalised for influenza between Dec 1, 2018, and Feb 28, 2019, were included. The diagnosis of COVID-19 (International Classification of Diseases [10th edition] codes U07.10, U07.11, U07.12, U07.14, or U07.15) or influenza (J09, J10, or J11) comprised primary, related, or associated diagnosis. Comparisons of risk factors, clinical characteristics, and outcomes between patients hospitalised for COVID-19 and influenza were done, with data also stratified by age group.
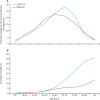
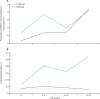
Findings: 89 530 patients with COVID-19 and 45 819 patients with influenza were hospitalised in France during the respective study periods. The median age of patients was 68 years (IQR 52-82) for COVID-19 and 71 years (34-84) for influenza. Patients with COVID-19 were more frequently obese or overweight, and more frequently had diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidaemia than patients with influenza, whereas those with influenza more frequently had heart failure, chronic respiratory disease, cirrhosis, and deficiency anaemia. Patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 more frequently developed acute respiratory failure, pulmonary embolism, septic shock, or haemorrhagic stroke than patients with influenza, but less frequently developed myocardial infarction or atrial fibrillation. In-hospital mortality was higher in patients with COVID-19 than in patients with influenza (15 104 [16·9%] of 89 530 vs 2640 [5·8%] of 45 819), with a relative risk of death of 2·9 (95% CI 2·8-3·0) and an age-standardised mortality ratio of 2·82. Of the patients hospitalised, the proportion of paediatric patients (<18 years) was smaller for COVID-19 than for influenza (1227 [1·4%] vs 8942 [19·5%]), but a larger proportion of patients younger than 5 years needed intensive care support for COVID-19 than for influenza (14 [2·3%] of 613 vs 65 [0·9%] of 6973). In adolescents (11-17 years), the in-hospital mortality was ten-times higher for COVID-19 than for influenza (five [1·1% of 458 vs one [0·1%] of 804), and patients with COVID-19 were more frequently obese or overweight.
Interpretation: The presentation of patients with COVID-19 and seasonal influenza requiring hospitalisation differs considerably. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 is likely to have a higher potential for respiratory pathogenicity, leading to more respiratory complications and to higher mortality. In children, although the rate of hospitalisation for COVID-19 appears to be lower than for influenza, in-hospital mortality is higher; however, low patient numbers limit this finding. These findings highlight the importance of appropriate preventive measures for COVID-19, as well as the need for a specific vaccine and treatment.
Funding: French National Research Agency.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
COVID-19 is not influenza.Lancet Respir Med. 2021 Mar;9(3):219-220. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30577-4. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Lancet Respir Med. 2021. PMID: 33341154 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Bewiesen: COVID-19 ≠ Influenza.MMW Fortschr Med. 2021 Feb;163(2):27. doi: 10.1007/s15006-021-9592-5. MMW Fortschr Med. 2021. PMID: 33527279 Free PMC article. German. No abstract available.
References
-
- Santé publique France L'épidémie de COVID-19 en chiffres. July 10, 2020. https://www.santepubliquefrance.fr/maladies-et-traumatismes/maladies-et-...
-
- Burn E, You SC, Sena A, et al. Deep phenotyping of 34,128 patients hospitalised with COVID-19 and a comparison with 81,596 influenza patients in America, Europe and Asia: an international network study. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.04.22.20074336. published online June 28. (preprint) - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

