Walking the line: mechanisms underlying directional mRNA transport and localisation in neurons and beyond
- PMID: 33341920
- PMCID: PMC8004493
- DOI: 10.1007/s00018-020-03724-3
Walking the line: mechanisms underlying directional mRNA transport and localisation in neurons and beyond
Abstract
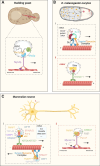
Messenger RNA (mRNA) localisation enables a high degree of spatiotemporal control on protein synthesis, which contributes to establishing the asymmetric protein distribution required to set up and maintain cellular polarity. As such, a tight control of mRNA localisation is essential for many biological processes during development and in adulthood, such as body axes determination in Drosophila melanogaster and synaptic plasticity in neurons. The mechanisms controlling how mRNAs are localised, including diffusion and entrapment, local degradation and directed active transport, are largely conserved across evolution and have been under investigation for decades in different biological models. In this review, we will discuss the standing of the field regarding directional mRNA transport in light of the recent discovery that RNA can hitchhike on cytoplasmic organelles, such as endolysosomes, and the impact of these transport modalities on our understanding of neuronal function during development, adulthood and in neurodegeneration.
Keywords: Axonal transport; Neurodegeneration; Vesicular traffic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interest to declare.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

