Agreement Between Standard Optical Coherence Tomography and Optical Coherence Tomography-Based Angiography in Estimating Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness
- PMID: 33342192
- PMCID: PMC7610055
- DOI: 10.4274/tjo.galenos.2020.18488
Agreement Between Standard Optical Coherence Tomography and Optical Coherence Tomography-Based Angiography in Estimating Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the agreement between optical coherence tomography (OCT) and OCT-based angiography (OCT-A) in estimating retinal nerve fiber layer thickness (RNFLT) and evaluate the associations between peripapillary vessel density (VD) and RNFLT measurements obtained with both devices.
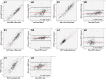
Materials and methods: The AngioVue (Optovue Inc., Fremont, CA, USA) and Spectralis (Heidelberg Engineering, Heidelberg, Germany) images of 325 patients were screened retrospectively. RNFLT values were recorded using both devices. The intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and Bland-Altman plots were obtained to investigate the agreement between the devices. Age- and intraocular pressure-corrected associations between VD and RNFLT measured by the two devices were analyzed using linear regression models.
Results: ICC revealed excellent agreement for global, superior, inferior, and temporal RNFLT and good agreement for the nasal quadrant (ICC=0.895, 0.936, 0.923, 0.887, and 0.614, respectively). The Bland-Altman plots showed poor agreement for all measurements with a large span of limits of agreement and significant proportional bias (p<0.05). VD was found to be strongly associated with the RNFLT measurements of both devices (p<0.001).
Conclusion: The disagreement between the devices should be considered in clinical practice, and the data should not be used interchangeably. The association of the peripapillary VD with RNFLT using both devices indicated that RNFLT assessed by the AngioVue could be used in glaucoma management along with VD.
Keywords: Glaucoma; agreement; angiography; coherence; optical.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Zhang Y, Wu LL, Yang YF. Potential of stratus optical coherence tomography for detecting early glaucoma in perimetrically normal eyes of open-angle glaucoma patients with unilateral visual field loss. J Glaucoma. 2010;19:61–65. - PubMed
-
- Kanamori A, Nakamura M, Escano MF, Seya R, Maeda H, Negi A. Evaluation of the glaucomatous damage on retinal nerve fiber layer thickness measured by optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol. 2003;135:513–520. - PubMed
-
- Yoo YC, Park KH. Comparison of optical coherence tomography and scanning laser polarimetry for detection of localized retinal nerve fiber layer defects. J Glaucoma. 2010;19:229–236. - PubMed
-
- Kim TW, Park UC, Park KH, Kim DM. Ability of stratus OCT to identify localized retinal nerve fiber layer defects in patients with normal standard automated perimetry results. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2007;48:1635–1641. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
