A systematic review assessing the under-representation of elderly adults in COVID-19 trials
- PMID: 33342426
- PMCID: PMC7749979
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-020-01954-5
A systematic review assessing the under-representation of elderly adults in COVID-19 trials
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) has caused a pandemic threatening millions of people worldwide. Yet studies specifically assessing the geriatric population are scarce. We aimed to examine the participation of elderly patients in therapeutic or prophylactic trials on COVID-19.
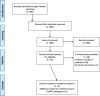
Methods: In this review, randomized controlled trials (RCTs; n = 12) comparing therapeutic or prophylactic interventions registered on preprint repositories and/or published since December 2019 were analyzed. We searched in PubMed, leading journals websites, and preprint repositories for RCTs and large observational studies. We aimed to describe the age of included patients, the presence of an upper age limit and of adjusted analyses on age, any exclusion criteria that could limit participation of elderly adults such as comorbidities, cognitive impairment, limitation of life expectancy; and the assessment of long-term outcomes such as the need of rehabilitation or institutionalization. Mean participant ages were reported and compared with observational studies.
Results: Twelve RCTs assessing drug therapy for COVID-19 were included. Mean age of patients included in RCTs was 56.3 years. An upper age limit was applied in three published trials (25%) and in 200/650 (31%) trials registered at clinicaltrials.gov . One trial reported a subgroup analysis in patients ≥65. Patients were excluded for liver-function abnormalities in eight trials, renal disease in six, cardiac disease or risk of torsade de pointes in five, and four for cognitive or mental criteria, which are frequent comorbidities in the oldest patients. Only three trials allowed a family member to provide consent. Patients enrolled in RCTs were on average 20 years younger than those included in large (n ≥ 1000) observational studies. Seven studies had as their primary outcome a clinical endpoint, but none reported cognitive, functional or quality of life outcomes or need for rehabilitation or long-term care facility placement.
Conclusions: Elderly patients are clearly underrepresented in RCTs, although they comprise the population hardest hit by the COVID-19 pandemic. Long-term outcomes such as the need of rehabilitation or institutionalization were not reported. Future investigations should target specifically this vulnerable population.
Keywords: COVID-19; Clinical trials, systematic review; Elderly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical