Improvement in Quality of Life with OnabotulinumtoxinA for Cervical Dystonia: POSTURe
- PMID: 33342445
- PMCID: PMC8527835
- DOI: 10.1017/cjn.2020.275
Improvement in Quality of Life with OnabotulinumtoxinA for Cervical Dystonia: POSTURe
Abstract
Introduction: Symptoms of cervical dystonia (CD) can vary in severity and cause significant pain. OnabotulinumtoxinA is an approved treatment for CD. This study assessed health-related quality of life (HRQoL) in patients with CD who received multiple onabotulinumtoxinA treatments.
Methods: This prospective, observational standard-of-care study was conducted at multiple neurology centers in Québec, Canada. Patients reported the health impact of CD using the Cervical Dystonia Impact Profile (CDIP)-58, before and after up to eight onabotulinumtoxinA treatments. Other measures included the Cervical Dystonia Severity Rating Scale by physician, employment status using the Work Productivity Questionnaire and pain using the Pain Numeric Rating Scale (PNRS). Adverse events (AEs) were recorded.
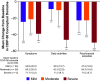
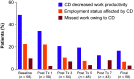
Results: Sixty-two patients were enrolled (safety population, n = 61; modified efficacy population, n = 58). Participants were mostly females who were employed; most (79.3%) had torticollis. In all, 21/62 patients (33.9%) discontinued the study. At the final visit, there was a statistically significant (p < 0.001) improvement in all eight CDIP-58 subscales, particularly head and neck symptoms (-31.0) and psychosocial functioning (-28.2). Employment increased from baseline (55%) to the end of the study (64%), and there was improvement in work productivity. There was a significant (p < 0.0001) reduction in pain measured by the PNRS, from -0.5 post-treatment 1 to -2.4 at end of study. AEs (neck pain, muscular weakness, dysphagia, nausea) were consistent with onabotulinumtoxinA use.
Conclusion: These real-world data indicate that after repeated, long-term use, onabotulinumtoxinA continues to be a safe and effective treatment for CD, improving HRQoL and work productivity.
L’onabotulinumtoxine A et l’amélioration de la qualité de vie des malades atteints de dystonie cervicale : POSTURe.
Introduction :: Les symptômes de la dystonie cervicale sont d’intensité variable et peuvent causer de la douleur importante; l’onabotulinumtoxine A est un médicament approuvé dans le traitement de ce trouble. L’étude visait à évaluer la qualité de vie liée à la santé (QVLS) chez des patients souffrant de dystonie cervicale et ayant reçu plusieurs injections d’onabotulinumtoxine A.
Méthode :: Il s’agit d’une étude d’observation, prospective, portant sur les soins usuels et réalisée dans plusieurs centres de neurologie, au Québec, au Canada. Les participants à l’étude ont fait état des répercussions de la dystonie cervicale sur leur qualité de vie, dans le questionnaire Cervical Dystonia Impact Profile (CDIP)58, avant et après l’administration de 1 à 8 injections au maximum d’onabotulinumtoxine A. D’autres questionnaires ont aussi été utilisés, notamment le Cervical Dystonia Severity Rating Scale, rempli par le médecin; le Work Productivity Questionnaire pour évaluer la situation de l’emploi; et le Pain Numeric Rating Scale (PNRS) pour évaluer la douleur. Ont également été consignés les effets indésirables (EI) du médicament.
Résultats :: Au total, 62 patients ont été retenus pour participer à l’étude (innocuité : population = 61 sujets; efficacité : population modifiée = 58 sujets). Il s’agissait en très grande partie de travailleuses; la plupart d’entre elles (79,3 %) souffraient de torticolis. Dans l’ensemble, 21 sujets sur 62 (33,9 %) se sont retirés de l’étude. À la dernière consultation, une amélioration statistiquement significative (p< 0,001) a été enregistrée dans les 8 sous-domaines d’évaluation du CDIP-58, notamment en ce qui concerne les symptômes affectant la tête et le cou (−31,0) et le fonctionnement psychosocial (−28,2). Une amélioration de la situation de l’emploi a été notée, du début (55 %) à la fin de l’étude (64 %), de même qu’une augmentation de la productivité au travail. D’après le questionnaire PNRS, il y a eu une réduction importante (p< 0,0001) de la douleur, résultat qui est passé de −0,5 après le 1er traitement à −2,4 à la fin de l’étude. Enfin, les EI (douleur cervicale, faiblesse musculaire, dysphagie, nausées) étaient compatibles avec ceux associés à l’emploi de l’onabotulinumtoxine A.
Conclusion :: Les données factuelles recueillies révèlent que l’emploi répété, voire prolongé, de l’onabotulinumtoxine A est un traitement sûr et efficace de la dystonie cervicale, tout en permettant une amélioration de la QVLS et de la productivité au travail.
Keywords: Cervical dystonia; OnabotulinumtoxinA; Patient-reported outcomes.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Concurrent onabotulinumtoxinA treatment of cervical dystonia and concomitant migraine.Headache. 2012 Sep;52(8):1219-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1526-4610.2012.02164.x. Epub 2012 May 18. Headache. 2012. PMID: 22607530 Clinical Trial.
-
Primary results from the cervical dystonia patient registry for observation of onabotulinumtoxina efficacy (CD PROBE).J Neurol Sci. 2015 Feb 15;349(1-2):84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2014.12.030. Epub 2014 Dec 27. J Neurol Sci. 2015. PMID: 25595221 Clinical Trial.
-
Cervical dystonia and pain: characteristics and treatment patterns from CD PROBE (Cervical Dystonia Patient Registry for Observation of OnabotulinumtoxinA Efficacy).J Neurol. 2014 Jul;261(7):1309-19. doi: 10.1007/s00415-014-7343-6. Epub 2014 Apr 22. J Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24752807 Free PMC article.
-
A mixed treatment comparison to compare the efficacy and safety of botulinum toxin treatments for cervical dystonia.J Neurol. 2016 Apr;263(4):772-80. doi: 10.1007/s00415-016-8050-2. Epub 2016 Feb 25. J Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26914922 Free PMC article.
-
Botulinum toxin B: a review of its therapeutic potential in the management of cervical dystonia.Drugs. 2002;62(4):705-22. doi: 10.2165/00003495-200262040-00011. Drugs. 2002. PMID: 11893235 Review.
Cited by
-
Intramuscular nerve distribution of the sternocleidomastoid muscle for the botulinum toxin injection.Surg Radiol Anat. 2024 Jun;46(6):905-913. doi: 10.1007/s00276-024-03367-0. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Surg Radiol Anat. 2024. PMID: 38684554
-
OnabotulinumtoxinA Dosing, Disease Severity, and Treatment Benefit in Patients With Cervical Dystonia: A Cohort Analysis From CD PROBE.Front Neurol. 2022 Jun 30;13:914486. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.914486. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35847221 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Langlois M, Richer F, Chouinard S. New perspectives on dystonia. Can J Neurol Sci. 2003;30(Suppl 1):S34–44. - PubMed
-
- Geyer HL, Bressman SB. The diagnosis of dystonia. Lancet Neurol. 2006;5(9):780–90. - PubMed
-
- Nijmeijer SW, Koelman JH, Standaar TS, Postma M, Tijssen MA. Cervical dystonia: improved treatment response to botulinum toxin after referral to a tertiary centre and the use of polymyography. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2013;19(5):533–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

