Telemedicine and the Use of Korean Medicine for Patients With COVID-19 in South Korea: Observational Study
- PMID: 33342765
- PMCID: PMC7817255
- DOI: 10.2196/20236
Telemedicine and the Use of Korean Medicine for Patients With COVID-19 in South Korea: Observational Study
Abstract
Background: COVID-19 was first reported in Wuhan, China, in December 2019, and it has since spread worldwide. The Association of Korean Medicine (AKOM) established the COVID-19 telemedicine center of Korean medicine (KM telemedicine center) in Daegu and Seoul.
Objective: The aim of this study was to describe the results of the KM telemedicine center and the clinical possibility of using herbal medicines for COVID-19.
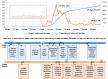
Methods: All procedures were conducted by voice call following standardized guidelines. The students in the reception group obtained informed consent from participants and they collected basic information. Subsequently, Korean Medicine doctors assessed COVID-19-related symptoms and prescribed the appropriate herbal medicine according to the KM telemedicine guidelines. The data of patients who completed the program by June 30, 2020, were analyzed.
Results: From March 9 to June 30, 2020, 2324 patients participated in and completed the KM telemedicine program. Kyung-Ok-Ko (n=2285) was the most prescribed herbal medicine, and Qingfei Paidu decoction (I and II, n=2053) was the second most prescribed. All COVID-19-related symptoms (headache, chills, sputum, dry cough, sore throat, fatigue, muscle pain, rhinorrhea, nasal congestion, dyspnea, chest tightness, diarrhea, and loss of appetite) improved after treatment (P<.001).
Conclusions: The KM telemedicine center has provided medical service to 10.8% of all patients with COVID-19 in South Korea (as of June 30, 2020), and it is still in operation. We hope that this study will help to establish a better health care system to overcome COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19; Korea; Korean medicine; guideline; herbal medicine; infectious disease; pandemic; telehealth; telemedicine.
©Soobin Jang, Dongsu Kim, Eunhee Yi, Gunhee Choi, Mideok Song, Eun-Kyoung Lee. Originally published in JMIR Public Health and Surveillance (http://publichealth.jmir.org), 19.01.2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report - 39. World Health Organization. [2020-12-30]. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio....
-
- Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Weekly Epidemiological Update and Weekly Operational Update. World Health Organization. [2020-12-30]. https://reliefweb.int/report/world/coronavirus-disease-covid-19-weekly-e....
-
- The Association of Korean medicine Recommendations on COVID-19 Korean medicine. 2020. [2020-12-30]. https://tinyurl.com/y55fde97.
-
- The KM Professor Council of Internal Medicine of the Respiratory System Clinical Guidelines on COVID-19 Korean Medicine. 2020. [2020-12-30]. https://tinyurl.com/y4yv8j7u.
-
- National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China [Notice on the Issuance of the New 7th Version of the COVID-19 Diagnosis and Treatment Guidelines] 2020. [2020-12-30]. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202003/46c9294a7dfe4cef80dc7f5912eb19....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

