Transhiatal isoperistaltic colon interposition without cervical oesophagostomy in long-gap oesophageal atresia
- PMID: 33342832
- PMCID: PMC8051634
- DOI: 10.4103/ajps.AJPS_95_17
Transhiatal isoperistaltic colon interposition without cervical oesophagostomy in long-gap oesophageal atresia
Abstract
Background: Oesophageal colonic interposition in oesophageal atresia (OA) patients is almost exclusively done as a staged operation with an initial oesophagostomy and gastrostomy followed by the definitive surgery months later. This study presents a series of patients in whom a cervical oesophagostomy was not performed before the substitution surgery.
Patients and methods: Records of EA patients were evaluated for those who underwent colon interposition without cervical oesophagostomy.
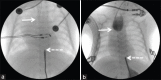
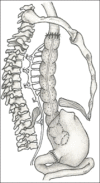
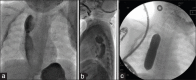
Results: There were five patients: three with pure EA and two with proximal tracheo-oesophageal fistula. A delayed primary repair could not be performed because of intra-abdominally located distal pouch. The mean age at the time of definitive operation was 5.54 (±2.7) months and the mean weight was 6.24 (±1.3) kg. A right or a left colonic segment was used for interposition keeping the proximal anastomosis within the thorax. The post-operative results were quite satisfactory within a median follow-up period of 33.2 months.
Conclusion: Avoiding cervical oesophagostomy and its inherent complications and drawbacks is possible in a subset of patients with long-gap EA who underwent colonic substitution surgery. This approach may be seen as an extension of the consensus that the native oesophagus should be preserved whenever possible, because it uses the native oesophagus in its entirety.
Keywords: Colon interposition; long gap; oesophageal atresia; oesophageal substitution; oesophagostomy.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures
Similar articles
-
A practical approach to the investigation and management of long gap oesophageal atresia.Indian J Pediatr. 1996 Nov-Dec;63(6):737-42. doi: 10.1007/BF02730921. Indian J Pediatr. 1996. PMID: 10830054
-
Long-term outcomes of oesophageal atresia without or with proximal tracheooesophageal fistula - Gross types A and B.J Pediatr Surg. 2017 Oct;52(10):1571-1575. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.04.021. Epub 2017 May 1. J Pediatr Surg. 2017. PMID: 28499713
-
Late life revision surgery for dilated colonic conduit in long gap oesophageal atresia.Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2018 Sep;100(7):e185-e187. doi: 10.1308/rcsann.2018.0120. Epub 2018 Aug 16. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2018. PMID: 30112934 Free PMC article.
-
[Cervical esophagogastrostomy dehiscence after gastric pull-up for type I esophageal atresia. Case report of a patient successfully treated with fibrin glue and a review of the literature].Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2003 Oct-Dec;68(4):288-92. Rev Gastroenterol Mex. 2003. PMID: 15125332 Review. Spanish.
-
Surgical management of oesophageal atresia.Paediatr Respir Rev. 2016 Jun;19:10-5. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2016.04.003. Epub 2016 Apr 21. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2016. PMID: 27217220 Review.
References
-
- Friedmacher F, Puri P. Delayed primary anastomosis for management of long-gap esophageal atresia: A meta-analysis of complications and long-term outcome. Pediatr Surg Int. 2012;28:899–906. - PubMed
-
- Séguier-Lipszyc E, Bonnard A, Aizenfisz S, Enezian G, Maintenant J, Aigrain Y, et al. The management of long gap esophageal atresia. J Pediatr Surg. 2005;40:1542–6. - PubMed
-
- Burgos L, Barrena S, Andrés AM, Martínez L, Hernández F, Olivares P, et al. Colonic interposition for esophageal replacement in children remains a good choice: 33-year median follow-up of 65 patients. J Pediatr Surg. 2010;45:341–5. - PubMed
-
- Long AM, Tyraskis A, Allin B, Burge DM, Knight M. Oesophageal atresia with no distal tracheoesophageal fistula: Management and outcomes from a population-based cohort. J Pediatr Surg. 2017;52:226–30. - PubMed
-
- Tannuri U, Tannuri AC. Should patients with esophageal atresia be submitted to esophageal substitution before they start walking? Dis Esophagus. 2011;24:25–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
