Detecting Mild Lower-limb Skeletal Muscle Fatigue with Stimulated-echo q-space Imaging
- PMID: 33342916
- PMCID: PMC8922348
- DOI: 10.2463/mrms.tn.2020-0096
Detecting Mild Lower-limb Skeletal Muscle Fatigue with Stimulated-echo q-space Imaging
Abstract
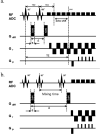
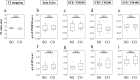
The feasibility of detecting mild exercise-related muscle fatigue via stimulated echo (STE) and q-space imaging (qsi) was evaluated. The right calves of seven healthy volunteers were subjected to mild exercise loading, and qsi was generated using spin echo (Δ: 45.6 ms) and three different STE (Δ: 114, 214, and 414 ms) acquisitions. We concluded that qsi with an increased STE diffusion time can detect mild fatigue in the gastrocnemius muscle.
Keywords: diffusion-weighted imaging; muscle fatigue; q-space imaging; stimulated echo.
Figures





References
-
- Hori M,, Fukunaga I,, Masutani Y,, et al. et al. Visualizing non-Gaussian diffusion: Clinical application of q-space imaging and diffusional kurtosis imaging of the brain and spine. Magn Reson Med Sci 2012; 11:221–233. - PubMed
-
- Cohen Y,, Assaf Y. High b-value q-space analyzed diffusion-weighted MRS and MRI in neuronal tissues – A technical review. NMR Biomed 2002; 15:516–542. - PubMed
-
- Nakashima D,, Fujita N,, Hata J,, et al. et al. Quantitative analysis of intervertebral disc degeneration using Q-space imaging in a rat model. J Orthop Res 2020; 38:2220–2229. - PubMed
-
- Sone Y,, Hata J,, Sera Y,, et al. et al. iShim and water excitation improves the signal-to-noise ratio on q-space imaging: A single-center clinical study. Open J Radiol 2018; 8:244–259.
-
- Cohen Y,, Anaby D,, Morozov D. Diffusion MRI of the spinal cord: From structural studies to pathology. NMR Biomed 2017; 30:e3592. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

