Pervasive prophage recombination occurs during evolution of spore-forming Bacilli
- PMID: 33343000
- PMCID: PMC8115142
- DOI: 10.1038/s41396-020-00854-1
Pervasive prophage recombination occurs during evolution of spore-forming Bacilli
Abstract
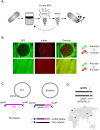
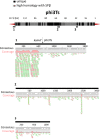
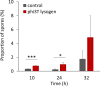
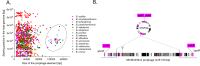
Phages are the main source of within-species bacterial diversity and drivers of horizontal gene transfer, but we know little about the mechanisms that drive genetic diversity of these mobile genetic elements (MGEs). Recently, we showed that a sporulation selection regime promotes evolutionary changes within SPβ prophage of Bacillus subtilis, leading to direct antagonistic interactions within the population. Herein, we reveal that under a sporulation selection regime, SPβ recombines with low copy number phi3Ts phage DNA present within the B. subtilis population. Recombination results in a new prophage occupying a different integration site, as well as the spontaneous release of virulent phage hybrids. Analysis of Bacillus sp. strains suggests that SPβ and phi3T belong to a distinct cluster of unusually large phages inserted into sporulation-related genes that are equipped with a spore-related genetic arsenal. Comparison of Bacillus sp. genomes indicates that similar diversification of SPβ-like phages takes place in nature. Our work is a stepping stone toward empirical studies on phage evolution, and understanding the eco-evolutionary relationships between bacteria and their phages. By capturing the first steps of new phage evolution, we reveal striking relationship between survival strategy of bacteria and evolution of their phages.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Knowles B, Silveira CB, Bailey BA, Barott K, Cantu VA, Cobián-Güemes AG, et al. Lytic to temperate switching of viral communities. Nature. 2016;531:466–70. - PubMed
-
- Azam AH, Tanji Y. Bacteriophage-host arm race: an update on the mechanism of phage resistance in bacteria and revenge of the phage with the perspective for phage therapy. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2019;103:2121–31. - PubMed
-
- Harrison E, Brockhurst MA. Ecological and evolutionary benefits of temperate phage: what does or doesn’t kill you makes you stronger. BioEssays. 2017;39:1700112. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

