Rapid microsphere-assisted peptide screening (MAPS) of promiscuous MHCII-binding peptides in Zika virus envelope protein
- PMID: 33343002
- PMCID: PMC7747769
- DOI: 10.1002/aic.16697
Rapid microsphere-assisted peptide screening (MAPS) of promiscuous MHCII-binding peptides in Zika virus envelope protein
Abstract
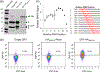
Despite promising developments in computational tools, peptide-class II MHC (MHCII) binding predictors continue to lag behind their peptide-class I MHC counterparts. Consequently, peptide-MHCII binding is often evaluated experimentally using competitive binding assays, which tend to sacrifice throughput for quantitative binding detail. Here, we developed a high-throughput semiquantitative peptide-MHCII screening strategy termed microsphere-assisted peptide screening (MAPS) that aims to balance the accuracy of competitive binding assays with the throughput of computational tools. Using MAPS, we screened a peptide library from Zika virus envelope (E) protein for binding to four common MHCII alleles (DR1, DR4, DR7, DR15). Interestingly, MAPS revealed a significant overlap between peptides that promiscuously bind multiple MHCII alleles and antibody neutralization sites. This overlap was also observed for rotavirus outer capsid glycoprotein VP7, suggesting a deeper relationship between B cell and CD4+ T cell specificity which can facilitate the design of broadly protective vaccines to Zika and other viruses.
Keywords: B cell epitopes; CD4+ T cell epitopes; MHC class II; Zika virus; peptide binding prediction; promiscuous peptide; rotavirus; vaccine.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures
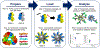

Similar articles
-
Rapid Identification of MHCII-Binding Peptides Through Microsphere-Assisted Peptide Screening (MAPS).Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2574:233-250. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2712-9_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36087205
-
Identification of immunodominant T cell epitopes induced by natural Zika virus infection.Front Immunol. 2023 Aug 29;14:1247876. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1247876. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37705976 Free PMC article.
-
Construction and Screening of an Antigen-Derived Peptide Library Displayed on Yeast Cell Surface for CD4+ T Cell Epitope Identification.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;2024:213-234. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-9597-4_13. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 31364052
-
MHCII-peptide presentation: an assessment of the state-of-the-art prediction methods.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 12;15:1293706. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1293706. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38646540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Revisiting nonclassical HLA II functions in antigen presentation: Peptide editing and its modulation.HLA. 2020 Oct;96(4):415-429. doi: 10.1111/tan.14007. Epub 2020 Aug 27. HLA. 2020. PMID: 32767512 Review.
Cited by
-
A high-throughput yeast display approach to profile pathogen proteomes for MHC-II binding.Elife. 2022 Jul 4;11:e78589. doi: 10.7554/eLife.78589. Elife. 2022. PMID: 35781135 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid Identification of MHCII-Binding Peptides Through Microsphere-Assisted Peptide Screening (MAPS).Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2574:233-250. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2712-9_11. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36087205
-
The Application of Single-Cell Technologies for Vaccine Development Against Viral Infections.Vaccines (Basel). 2025 Jun 26;13(7):687. doi: 10.3390/vaccines13070687. Vaccines (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40733664 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dai L, Song J, Lu X, et al. Structures of the Zika virus envelope protein and its complex with a Flavivirus broadly protective antibody. Cell Host Microbe 2016;19(5):696–704. - PubMed
-
- Stettler K, Beltramello M, Espinosa DA, et al. Specificity, cross-reactivity, and function of antibodies elicited by Zika virus infection. Science 2016;353(6301):823–826. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
