QTL mapping for micronutrients concentration and yield component traits in a hexaploid wheat mapping population
- PMID: 33343062
- PMCID: PMC7729826
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcs.2019.05.008
QTL mapping for micronutrients concentration and yield component traits in a hexaploid wheat mapping population
Abstract
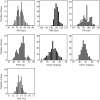
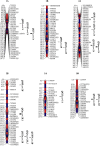
Bread wheat is a major staple cereal provides more than 20% of dietary energy and protein supply to global population. However, with increasing population growth, the problem of nutritional deficiencies is increasingly affecting the health of resource people with predominantly cereal-based diet. Therefore, the development of wheat genotypes with micronutrient-dense grains along with high-yield potential is one of the major priorities of wheat biofortification program at CIMMYT. We conducted a QTL mapping study using a recombinant inbred line (RIL) population derived from a cross between a Chinese parental line with highGZnC and a Mexican commercial bread wheat cultivar Roelfs F2007 to identify QTLs that could potentially be integrated in mineral nutrient concentrations and agronomic-related traits breeding. We evaluated 200 RIL lines for mineral nutrient concentrations and agronomic-related traits over two years. A total of 60 QTLs were detected, of which 10 QTLs for GZnC, 9 for GFeC, 5 for GPC and 36 for agronomic-related traits. Moreover, a total of 55 promising candidate genes were identified from the list of associated markers for GFeC and GZnC using the recently annotated wheat genome sequence. We identified the promising genomic regions with high mineral nutrient concentrations and acceptable yield potential, which are good resource for further use in wheat biofortification breeding programs.
Keywords: Agronomic-related traits; GFeC, Grain iron concentration; GPC, Grain protein concentration; GZnC, Grain zinc concentration; Grain mineral nutrient concentration; HD, Heading date; MD, Maturity date; PH, Plant height; PVE, Phenotypic variation explained; QTL mapping; QTL, Quantitative trait loci; TKW, Thousand kernel weight; Wheat biofortification.
© 2019 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Braun H.J., Atlin G., Payne T. Multi-location testing as a tool to identify plant response to global climate change. Climate change and crop production. 2010;1:115–138.
-
- Cakmak I., Ozkan H., Braun H.J., Welch R.M., Romheld V. Zinc and iron concentrations in seeds of wild, primitive, and modern wheats. Food Nutr. Bull. 2000;21:401–403.
-
- Cui F., Li J., Ding A., Zhao C., Wang L., Wang X., Li S., Bao Y., Li X., Feng D., Kong L., Wang H. Conditional QTL mapping for plant height with respect to the length of the spike and internode in two mapping populations of wheat. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2011;122:1517–1536. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
