Mechanisms Underlying the Antidepressant Effect of Acupuncture via the CaMK Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33343309
- PMCID: PMC7746547
- DOI: 10.3389/fnbeh.2020.563698
Mechanisms Underlying the Antidepressant Effect of Acupuncture via the CaMK Signaling Pathway
Abstract
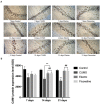
The CaMK pathway has been proven to play an important role in regulating cognitive function and emotional response. Acupuncture through the CaMK pathway improves depression-like behavior and the molecular mechanism related to its antidepressant remains to be explored. In this study, we aimed to determine whether the ability of acupuncture at Baihui (GV20) and Shenting (GV24) points to treat depression is related to the regulation of key proteins in the CaMK pathway. A rat model of depression was induced by chronic unpredicted mild stress (CUMS). Model rats in the electroacupuncture group were subjected to acupuncture at the Baihui (GV20) and Shenting (GV24) acupoints once a day for 20 min. Model rats in the fluoxetine group were gavaged with fluoxetine (1.8 mg/kg). Immunohistochemistry and Western blotting assays were used to evaluate immunoreactivity for and the protein expression levels of CaMKII, CaMKIV, and CaM. The results showed that electroacupuncture had a significant effect in rats with depression. Electroacupuncture and fluoxetine regulated the expression of key proteins in the CaMK signaling pathway, which is related to depression, in the hippocampi of rats. This indicates that acupuncture at Baihui (GV20) and Shenting (GV24) may alleviate depressive symptoms and reduce work- and life-related burdens and stress by regulating the CaMK signaling pathway.
Keywords: Baihui; CAMK signaling pathway; Shenting; depression; electroacupuncture.
Copyright © 2020 Bai, Zhang, Cui, Li, Gao, Wang, Jia, Zhang, Sun, Zou and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

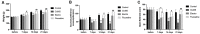

Similar articles
-
Electroacupuncture of Baihui and Shenting ameliorates cognitive deficits via Pten/Akt pathway in a rat cerebral ischemia injury model.Front Neurol. 2022 Aug 19;13:855362. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.855362. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36062010 Free PMC article.
-
Electroacupuncture improves learning and memory functions in a rat cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury model through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway activation.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Jun;16(6):1011-1016. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.300454. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33269744 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on mechanisms of acupuncture underlying improvement of CUMS-induced depression in rats based on tandem mass spectrometry proteomics technique].Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023 Jun 25;48(6):533-40. doi: 10.13702/j.1000-0607.20220454. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu. 2023. PMID: 37385783 Chinese.
-
Manual acupuncture enhanced therapeutic efficacy in vascular dementia rat model: systematic review and network meta-analysis.Syst Rev. 2025 Apr 5;14(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13643-025-02821-3. Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40186311 Free PMC article.
-
Possible antidepressant mechanism of acupuncture: targeting neuroplasticity.Front Neurosci. 2025 Feb 13;19:1512073. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2025.1512073. eCollection 2025. Front Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40018358 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Acupuncture Is Effective at Reducing the Risk of Stroke in Patients with Migraines: A Real-World, Large-Scale Cohort Study with 19-Years of Follow-Up.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 17;20(3):1690. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20031690. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36767053 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Targeting Mitochondrial Homeostasis: The Role of Acupuncture in Depression Treatment.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023 Aug 1;19:1741-1753. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S421540. eCollection 2023. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2023. PMID: 37546517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms of acupuncture in treating depression: a review.Chin Med. 2025 Mar 3;20(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01080-7. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40033393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of electroacupuncture on anxiety in patients with obesity: a protocol for a randomised, blinded, sham-controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2025 Jul 15;15(7):e093916. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-093916. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40664406 Free PMC article.
-
The Calcium/Calmodulin-Dependent Kinases II and IV as Therapeutic Targets in Neurodegenerative and Neuropsychiatric Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 21;22(9):4307. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094307. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33919163 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ampuero E., Rubio F. J., Falcon R., Sandoval M., Diaz-Veliz G., Gonzalez R. E., et al. . (2010). Chronic fluoxetine treatment induces structural plasticity and selective changes in glutamate receptor subunits in the rat cerebral cortex. Neuroscience 169, 98–108. 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.04.035 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

