Transient Enhanced GluA2 Expression in Young Hippocampal Neurons of a Fragile X Mouse Model
- PMID: 33343326
- PMCID: PMC7745073
- DOI: 10.3389/fnsyn.2020.588295
Transient Enhanced GluA2 Expression in Young Hippocampal Neurons of a Fragile X Mouse Model
Abstract
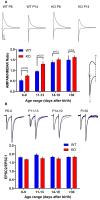
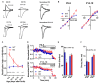
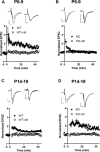
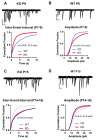
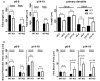
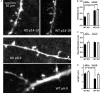
AMPA-type glutamate receptors (AMPARs) are tetrameric ligand-gated channels made up of combinations of GluA1-4 subunits and play important roles in synaptic transmission and plasticity. Here, we have investigated the development of AMPAR-mediated synaptic transmission in the hippocampus of the Fmr1 knock-out (KO) mouse, a widely used model of Fragile X syndrome (FXS). FXS is the leading monogenic cause of intellectual disability and autism spectrum disorders (ASD) and it is considered a neurodevelopmental disorder. For that reason, we investigated synaptic properties and dendritic development in animals from an early stage when synapses are starting to form up to adulthood. We found that hippocampal CA1 pyramidal neurons in the Fmr1-KO mouse exhibit a higher AMPAR-NMDAR ratio early in development but reverses to normal values after P13. This increase was accompanied by a larger presence of the GluA2-subunit in synaptic AMPARs that will lead to altered Ca2+ permeability of AMPARs that could have a profound impact upon neural circuits, learning, and diseases. Following this, we found that young KO animals lack Long-term potentiation (LTP), a well-understood model of synaptic plasticity necessary for proper development of circuits, and exhibit an increased frequency of spontaneous miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents, a measure of synaptic density. Furthermore, post hoc morphological analysis of recorded neurons revealed altered dendritic branching in the KO group. Interestingly, all these anomalies are transitory and revert to normal values in older animals. Our data suggest that loss of FMRP during early development leads to temporary upregulation of the GluA2 subunit and this impacts synaptic plasticity and altering morphological dendritic branching.
Keywords: FMR 1 gene; LTP (long term potentiation); NMDAR (NMDA receptor); circuit; dendritic spines and memory; fragile X mental retardation protein; glutamate receptor (AMPAR); synapses.
Copyright © 2020 Banke and Barria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of GluN2A NMDA receptors ameliorates synaptic plasticity deficits in the Fmr1-/y mouse model.J Physiol. 2018 Oct;596(20):5017-5031. doi: 10.1113/JP276304. Epub 2018 Sep 19. J Physiol. 2018. PMID: 30132892 Free PMC article.
-
Impaired synaptic incorporation of AMPA receptors in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Nov 9;16:1258615. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1258615. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38025260 Free PMC article.
-
CPEB3-dependent increase in GluA2 subunits impairs excitatory transmission onto inhibitory interneurons in a mouse model of fragile X.Cell Rep. 2022 Jun 7;39(10):110853. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110853. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35675768 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of neuronal PKA signaling through AKAP targeting dynamics.Eur J Cell Biol. 2006 Jul;85(7):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcb.2006.01.010. Epub 2006 Feb 28. Eur J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16504338 Review.
-
BDNF in fragile X syndrome.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Jan;76 Pt C:729-36. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.05.018. Epub 2013 May 29. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 23727436 Review.
Cited by
-
FMRP Controls Neuronal Architecture and Synaptic Content of NMDA Receptors in Cultured Hippocampal Neurons.J Mol Neurosci. 2025 Apr 2;75(2):44. doi: 10.1007/s12031-025-02325-8. J Mol Neurosci. 2025. PMID: 40172581 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotection Against NMDA-Induced Retinal Damage by Philanthotoxin-343 Involves Reduced Nitrosative Stress.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 14;12:798794. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.798794. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34970151 Free PMC article.
-
Cage effects on synaptic plasticity and its modulation in a mouse model of fragile X syndrome.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024 Jul 29;379(1906):20230484. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2023.0484. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38853552 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of MDI-114215: A Potent and Selective LIMK Inhibitor To Treat Fragile X Syndrome.J Med Chem. 2025 Jan 9;68(1):719-752. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c02694. Epub 2024 Dec 22. J Med Chem. 2025. PMID: 39711116 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory dysfunction and altered cortical excitability in the mouse model of Fragile X Syndrome.Biol Res. 2025 Apr 24;58(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s40659-024-00582-2. Biol Res. 2025. PMID: 40275427 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

