Associations of Platelet Count with Inflammation and Response to Anti-TNF-α Therapy in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
- PMID: 33343345
- PMCID: PMC7741170
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.559593
Associations of Platelet Count with Inflammation and Response to Anti-TNF-α Therapy in Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis
Abstract
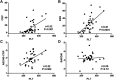
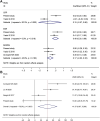
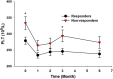
Background: Increased platelet count has been reported in ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients, but its clinical significance is still largely elusive. The objective of this study was to evaluate the clinical role of platelet count in AS patients, especially its impact on treatment outcomes. Methods: A case-control study containing 35 AS patients receiving anti-tumor necrosis factor-α (anti-TNF-α) therapy and 45 healthy controls was performed, and AS patients were followed at least 6 months after anti-TNF-α therapy. A systematic review and meta-analysis of studies containing relevant data on outcomes of interest was also performed. Results: AS patients had significantly higher platelet count than controls (p = 0.0001), and the significantly increased platelet count in AS patients was confirmed in a meta-analysis of 14 studies involving 1,223 AS patients and 913 controls (mean difference = 39.61, 95% CI 27.89-51.34, p < 0.001). Besides, platelet count was significantly correlated with ESR (p < 0.001) and was moderately correlated with ASDAS-CRP score (p = 0.002). Moreover, anti-TNF-α therapy could reduce platelet count in AS patients at the first month and the effect was maintained through the treatment duration. In the prospective follow-up study of those 35 AS patients, those responders to anti-TNF-α therapy had significantly lower platelet count than nonresponders (p = 0.015). Logistic regression analysis suggested that lower platelet count was associated with higher possibility of achieving good response to anti-TNF-α therapy in AS patients (odds ratio = 2.26; 95% CI = 1.06-4.82; p = 0.035). Conclusion: This study suggested that platelet count was associated with inflammation severity and treatment outcomes in AS patients, and elevated platelet count was a promising biomarker of poorer response to anti-TNF-α therapy. The findings above need to be validated in more future studies.
Keywords: ankylosing spondylitis; anti-TNF-α therapy; biomarkers; platelet count; treatment outcomes.
Copyright © 2020 Qian, Chen, Wang, Yuan, Chen, Liu and Shi.
Figures


References
-
- Akboga M. K., Canpolat U., Yuksel M., Yayla C., Yilmaz S., Turak O., et al. (2016). Platelet to lymphocyte ratio as a novel indicator of inflammation is correlated with the severity of metabolic syndrome: a single center large-scale study. Platelets 27, 178–183. 10.3109/09537104.2015.1064518 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Andrianova I. A., Ponomareva A. A., Mordakhanova E. R., Le Minh G., Daminova A. G., Nevzorova T. A., et al. (2019). In systemic lupus erythematosus anti-dsDNA antibodies can promote thrombosis through direct platelet activation. J. Autoimmun. 107, 102355 10.1016/j.jaut.2019.102355 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

