Pharmacological Effects of Salvianolic Acid B Against Oxidative Damage
- PMID: 33343348
- PMCID: PMC7741185
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.572373
Pharmacological Effects of Salvianolic Acid B Against Oxidative Damage
Abstract
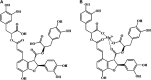
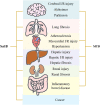
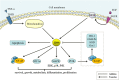
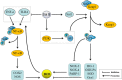
Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) is one of the main active ingredients of Salvia miltiorrhiza, with strong antioxidant effects. Recent findings have shown that Sal B has anti-inflammatory, anti-apoptotic, anti-fibrotic effects and can promote stem cell proliferation and differentiation, and has a beneficial effect on cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, aging, and liver fibrosis. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) include oxygen free radicals and oxygen-containing non-free radicals. ROS can regulate cell proliferation, survival, death and differentiation to regulate inflammation, and immunity, while Sal B can scavenge oxygen free radicals by providing hydrogen atoms and reduce the production of oxygen free radicals and oxygen-containing non-radicals by regulating the expression of antioxidant enzymes. The many pharmacological effects of Sal B may be closely related to its elimination and inhibition of ROS generation, and Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2/Kelch-like ECH-related protein 1 may be the core link in its regulation of the expression of antioxidant enzyme to exert its antioxidant effect. What is confusing and interesting is that Sal B exhibits the opposite mechanisms in tumors. To clarify the specific target of Sal B and the correlation between its regulation of oxidative stress and energy metabolism homeostasis will help to further understand its role in different pathological conditions, and provide a scientific basis for its further clinical application and new drug development. Although Sal B has broad prospects in clinical application due to its extensive pharmacological effects, the low bioavailability is a serious obstacle to further improving its efficacy in vivo and promoting clinical application. Therefore, how to improve the availability of Sal B in vivo requires the joint efforts of many interdisciplinary subjects.
Keywords: Keap1; Nrf2; ROS; oxidative damage; salvianolic acid B.
Copyright © 2020 Xiao, Liu, Mu, Zhang, Wang, Zhao, Chen and Liu.
Figures
References
-
- Ba J., Peng H., Chen Y., Gao Y. (2014). Effects and mechanism analysis of vascular endothelial growth factor and salvianolic acid B on 125I-low density lipoprotein permeability of the rabbit aortary endothelial cells. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 70 (3), 1533–1538. 10.1007/s12013-014-0089-z - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

