Comparative Remission Rates and Tolerability of Drugs for Generalised Anxiety Disorder: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis of Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 33343351
- PMCID: PMC7741609
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.580858
Comparative Remission Rates and Tolerability of Drugs for Generalised Anxiety Disorder: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-analysis of Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
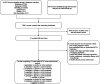
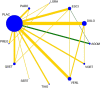
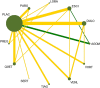
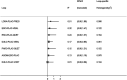
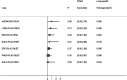
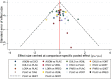
Background: Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is one of the most common psychiatric disorders associated with substantial dysfunction and socioeconomic burden. Pharmacotherapy is the first choice for GAD. Remission [Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAM-A) score ≤7] is regarded as a crucial treatment goal for patients with GAD. There is no up-to-date evidence to compare remission rate and tolerability of all available drugs by using network meta-analysis. Therefore, the goal of our study is to update evidence and determine the best advantageous drugs for GAD in remission rate and tolerability profiles. Method: We performed a systematic review and network meta-analysis of double-blind randomized controlled trials (RCTs). We searched PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, Chinese National Knowledge Infrastructure, wanfang data, China Biology Medicine and ClinicalTrials.gov from their inception to March 2020 to identify eligible double-blind, RCTs reporting the outcome of remission in adult patients who received any pharmacological treatment for GAD. Two reviewers independently assessed quality of included studies utilizing the Cochrane Collaboration's risk of bias tool as described in Cochrane Collaboration Handbook and extracted data from all manuscripts. Our outcomes were remission rate (proportion of participants with a final score of seven or less on HAM-A) and tolerability (treatments discontinuations due to adverse events). We calculated summary odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) of each outcome via pairwise and network meta-analysis with random effects. Results: Overall, 30 studies were included, comprising 32 double-blind RCTs, involving 13,338 participants diagnosed as GAD by DSM-IV criteria. Twenty-eight trials were rated as moderate risk of bias, four trials as low. For remission rate, agomelatine (OR 2.70, 95% CI 1.74-4.19), duloxetine (OR 1.88, 95% CI 1.47-2.40), escitalopram (OR 2.03, 95% CI 1.48-2.78), paroxetine (OR 1.74, 95% CI 1.25-2.42), quetiapine (OR 1.88, 95% CI 1.39-2.55), and venlafaxine (OR 2.28, 95% CI 1.69-3.07) were superior to placebo. For tolerability, sertraline, agomelatine, vortioxetine, and pregabalin were found to be comparable to placebo. However, the others were worse than placebo in terms of tolerability, with ORs ranging between 1.86 (95% CI 1.25-2.75) for tiagabine and 5.98 (95% CI 2.41-14.87) for lorazepam. In head-to-head comparisons, agomelatine, duloxetine, escitalopram, quetiapine, and venlafaxine were more efficacious than tiagabine in terms of remission rate, ORs from 1.66 (95% CI 1.04-2.65) for duloxetine to 2.38 (95% CI 1.32-4.31) for agomelatine. We also found that agomelatine (OR 2.08, 95% CI 1.15-3.75) and venlafaxine (OR 1.76, 95% CI 1.08-2.86) were superior to vortioxetine. Lorazepam and quetiapine were poorly tolerated when compared with other drugs. Conclusions: Of these interventions, only agomelatine manifested better remission with relatively good tolerability but these results were limited by small sample sizes. Duloxetine, escitalopram, venlafaxine, paroxetine, and quetiapine showed better remission but were poorly tolerated.
Keywords: generalized anxiety disorder; network meta-analysis; pharmacotherapy; remission rate; tolerability.
Copyright © 2020 Kong, Deng, Wan, Zhou, Zhou, Song and Wang.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Pharmacological treatments for generalised anxiety disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis.Lancet. 2019 Feb 23;393(10173):768-777. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)31793-8. Epub 2019 Jan 31. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 30712879
-
Efficacy and tolerability of short-term duloxetine treatment in adults with generalized anxiety disorder: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2018 Mar 20;13(3):e0194501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0194501. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29558528 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy of antidepressant medication for adolescent depression: a network meta-analysis and systematic review.BMC Psychiatry. 2025 May 10;25(1):471. doi: 10.1186/s12888-025-06941-x. BMC Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 40349006 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and tolerability of antidepressant drugs in treatment of depression in children and adolescents: a network meta-analysis.Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022 Aug 1;51(4):480-490. doi: 10.3724/zdxbyxb-2022-0145. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2022. PMID: 37202104 Free PMC article. English.
-
Short-term efficacy and tolerability of venlafaxine extended release in adults with generalized anxiety disorder without depression: A meta-analysis.PLoS One. 2017 Oct 5;12(10):e0185865. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0185865. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28982121 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Potential and Limitation of Serotonin Type 7 Receptor Modulation.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2070. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032070. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768393 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vortioxetine as a new frontier in the treatment of chronic neuropathic pain: a review and update.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2021 Sep 3;11:20451253211034320. doi: 10.1177/20451253211034320. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34497709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of the Chinese herbal medicine Xiao Yao San for treating anxiety: a systematic review with meta-analysis and trial sequential analysis.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Oct 12;14:1169292. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1169292. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37905203 Free PMC article.
-
Agomelatine in pediatric patients with moderate to severe major depressive disorder: an open-label extension study.Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2025 May;34(5):1603-1614. doi: 10.1007/s00787-024-02587-4. Epub 2024 Oct 10. Eur Child Adolesc Psychiatry. 2025. PMID: 39390266 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Agomelatine for the treatment of generalized anxiety disorder: focus on its distinctive mechanism of action.Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2022 Jun 30;12:20451253221105128. doi: 10.1177/20451253221105128. eCollection 2022. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35795687 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alaka K. J., Noble W., Montejo A., Dueñas H., Munshi A., Strawn J. R., et al. (2014). Efficacy and safety of duloxetine in the treatment of older adult patients with generalized anxiety disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatr. 29, 978–986. 10.1002/gps.4088 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

