Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Ameliorates Cardiac Remodelling After Myocardial Infarction Through PI3K/AKT Pathway in Mice
- PMID: 33343353
- PMCID: PMC7747856
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.585984
Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Ameliorates Cardiac Remodelling After Myocardial Infarction Through PI3K/AKT Pathway in Mice
Abstract
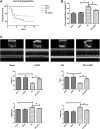
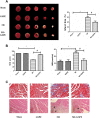
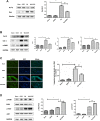
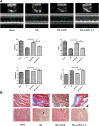
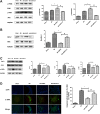
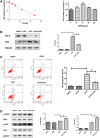
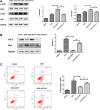
Myocardial infarction is one of the most serious fatal diseases in the world, which is due to acute occlusion of coronary arteries. Grape seed proanthocyanidin extract (GSPE) is an active compound extracted from grape seeds that has anti-oxidative, anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor pharmacological effects. Natural products are cheap, easy to obtain, widely used and effective. It has been used to treat numerous diseases, such as cancer, brain injury and diabetes complications. However, there are limited studies on its role and associated mechanisms in myocardial infarction in mice. This study showed that GSPE treatment in mice significantly reduced cardiac dysfunction and improved the pathological changes due to MI injury. In vitro, GSPE inhibited the apoptosis of H9C2 cells after hypoxia culture, resulting in the expression of Bax decreased and the expression of Bcl-2 increased. The high expression of p-PI3K and p-AKT was detected in MI model in vivo and in vitro. The use of the specific PI3K/AKT pathway inhibitor LY294002 regressed the cardio-protection of GSPE. Our results showed that GSPE could improve the cardiac dysfunction and remodeling induced by MI and inhibit cardiomyocytes apoptosis in hypoxic conditions through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway.
Keywords: apoptosis; cardiac function; grape seed proanthocyanidin extract; myocardial fibrosis; myocardial infarction; pi3k/akt pathway.
Copyright © 2020 Ruan, Jin, Zeng, Ren, Xie, Ji, Wu, Wu and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abbruzzese G., Morón-Oset J., Díaz-Castroverde S., García-Font N., Roncero C., López-Muñoz F., et al. (2020). Neuroprotection by phytoestrogens in the model of deprivation and resupply of oxygen and glucose in vitro: the contribution of autophagy and related signaling mechanisms. Antioxidants 9 (6), 545 10.3390/antiox9060545 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

