Simultaneous CRISPR/Cas9 Editing of Three PPO Genes Reduces Fruit Flesh Browning in Solanum melongena L
- PMID: 33343607
- PMCID: PMC7744776
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2020.607161
Simultaneous CRISPR/Cas9 Editing of Three PPO Genes Reduces Fruit Flesh Browning in Solanum melongena L
Abstract
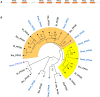
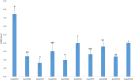
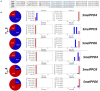
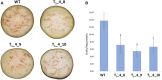
Polyphenol oxidases (PPOs) catalyze the oxidization of polyphenols, which in turn causes the browning of the eggplant berry flesh after cutting. This has a negative impact on fruit quality for both industrial transformation and fresh consumption. Ten PPO genes (named SmelPPO1-10) were identified in eggplant thanks to the recent availability of a high-quality genome sequence. A CRISPR/Cas9-based mutagenesis approach was applied to knock-out three target PPO genes (SmelPPO4, SmelPPO5, and SmelPPO6), which showed high transcript levels in the fruit after cutting. An optimized transformation protocol for eggplant cotyledons was used to obtain plants in which Cas9 is directed to a conserved region shared by the three PPO genes. The successful editing of the SmelPPO4, SmelPPO5, and SmelPPO6 loci of in vitro regenerated plantlets was confirmed by Illumina deep sequencing of amplicons of the target sites. Besides, deep sequencing of amplicons of the potential off-target loci identified in silico proved the absence of detectable non-specific mutations. The induced mutations were stably inherited in the T1 and T2 progeny and were associated with a reduced PPO activity and browning of the berry flesh after cutting. Our results provide the first example of the use of the CRISPR/Cas9 system in eggplant for biotechnological applications and open the way to the development of eggplant genotypes with low flesh browning which maintain a high polyphenol content in the berries.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas 9; eggplant; gene editing; knock-out; polyphenol oxydase.
Copyright © 2020 Maioli, Gianoglio, Moglia, Acquadro, Valentino, Milani, Prohens, Orzaez, Granell, Lanteri and Comino.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Abdelwahd R., Hakam N., Labhilili M., Udupa S. M. (2008). Use of an adsorbent and antioxidants to reduce the effects of leached phenolics in in vitro plantlet regeneration of faba bean. African J. Biotechnol. 7, 997–1002.
-
- Bachem C. W. B., Speckmann G. J., Van der Linde Piet C. G., Verheggen F. T. M., Hunt M. D., Steffens J. C., et al. (1994). Antisense expression of polyphenol oxidase genes inhibits enzymatic browning in potato tubers. Bio/Technology. 12, 1101–1105. 10.1038/nbt1194-1101 - DOI

