Impact of proton pump inhibitors on clinical outcomes in patients after acute myocardial infarction: a propensity score analysis from China Acute Myocardial Infarction (CAMI) registry
- PMID: 33343644
- PMCID: PMC7729183
- DOI: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2020.11.008
Impact of proton pump inhibitors on clinical outcomes in patients after acute myocardial infarction: a propensity score analysis from China Acute Myocardial Infarction (CAMI) registry
Abstract
Background: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) are recommended by the latest guidelines to reduce the risk of bleeding in acute myocardial infarction (AMI) patients treated with dual antiplatelet therapy (DAPT). However, previous pharmacodynamic and clinical studies have reported controversial results on the interaction between PPI and the P2Y12 inhibitor clopidogrel. We investigated the impact of PPIs use on in-hospital outcomes in AMI patients, aiming to provide a new insight on the value of PPIs.
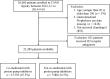
Methods: A total of 23, 380 consecutive AMI patients who received clopidogrel with or without PPIs in the China Acute Myocardial Infarction (CAMI) registry were analyzed. The primary endpoint was major adverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events (MACCE) defined as a composite of in-hospital cardiac death, re-infarction and stroke. Propensity score matching (PSM) was used to control potential baseline confounders. Multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed to evaluate the effect of PPIs use on MACCE and gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB).
Results: Among the whole AMI population, a large majority received DAPT and 67.5% were co-medicated with PPIs. PPIs use was associated with a decreased risk of MACCE (Before PSM OR: 0.857, 95% CI: 0.742-0.990, P = 0.0359; after PSM OR: 0.862, 95% CI: 0.768-0.949, P = 0.0245) after multivariate adjustment. Patients receiving PPIs also had a lower risk of cardiac death but a higher risk of complicating with stroke. When GIB occurred, an alleviating trend of GIB severity was observed in PPIs group.
Conclusions: Our study is the first nation-wide large-scale study to show evidence on PPIs use in AMI patients treated with DAPT. We found that PPIs in combination with clopidogrel was associated with decreased risk for MACCE in AMI patients, and it might have a trend to mitigate GIB severity. Therefore, PPIs could become an available choice for AMI patients during hospitalization.
Keywords: Acute myocardial infarction; Clopidogrel; Drug interaction; Propensity score matching; Proton-pump inhibitors.
Copyright and License information: Journal of Geriatric Cardiology 2020.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Clinical Impact of Proton Pump Inhibitors When Co-Administered With Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Patients Having Acute Myocardial Infarction With Low Risk of Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Insights From the China Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Sep 22;8:685072. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.685072. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34631809 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Proton-pump Inhibitors on the Pharmacodynamic Effect and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Receiving Dual Antiplatelet Therapy after Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: A Propensity Score Analysis.Chin Med J (Engl). 2017 Dec 20;130(24):2899-2905. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.220304. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017. PMID: 29237921 Free PMC article.
-
Appropriateness of gastrointestinal prophylaxis use during hospitalization in patients with acute myocardial infarction: Analysis from the China Acute Myocardial Infarction Registry.Clin Cardiol. 2021 Jan;44(1):43-50. doi: 10.1002/clc.23449. Epub 2020 Nov 19. Clin Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33211327 Free PMC article.
-
Drug interaction between clopidogrel and proton pump inhibitors.Pharmacotherapy. 2010 Mar;30(3):275-89. doi: 10.1592/phco.30.3.275. Pharmacotherapy. 2010. PMID: 20180611 Review.
-
Concomitant use of proton pump inhibitors and dual antiplatelet therapy for cardiovascular outcomes.Minerva Endocrinol. 2017 Sep;42(3):228-237. doi: 10.23736/S0391-1977.16.02571-2. Epub 2016 Nov 3. Minerva Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 27808485 Review.
Cited by
-
The Efficacy and Safety of Proton Pump Inhibitors Combining Dual Antiplatelet Therapy in Patients with Coronary Intervention: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Trial Sequential Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Aug 9;24(8):230. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2408230. eCollection 2023 Aug. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39076718 Free PMC article.
-
Risk of stroke associated with proton pump inhibitor use among individuals with and without pre-existing cardiovascular diseases: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025 Jan 29;20(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s13019-024-03161-4. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2025. PMID: 39881328 Free PMC article.
-
The application of proton pump inhibitors in cardiovascular disease needs to be individualized.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022 Dec;36(6):1247-1248. doi: 10.1007/s10557-022-07395-z. Epub 2022 Oct 22. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2022. PMID: 36272044 No abstract available.
-
Gastroprotection during long-term dual antiplatelet therapy: to give or not to give?J Geriatr Cardiol. 2021 Nov 28;18(11):973-974. doi: 10.11909/j.issn.1671-5411.2021.11.008. J Geriatr Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34908932 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Co-prescription of Dual-Antiplatelet Therapy and Proton Pump Inhibitors: Current Guidelines.Cureus. 2022 Feb 3;14(2):e21885. doi: 10.7759/cureus.21885. eCollection 2022 Feb. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 35273851 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Nikolsky E, Stone GW, Kirtane AJ, et al. Gastrointestinal bleeding in patients with acute coronary syndromes: incidence, predictors, and clinical implications: analysis from the ACUITY (Acute Catheterization and Urgent Intervention Triage Strategy) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2009:1293–1302. - PubMed
-
- Valgimigli M, Costa F, Lokhnygina Y, et al. Trade-off of myocardial infarction vs. bleeding types on mortality after acute coronary syndrome: lessons from the Thrombin Receptor Antagonist for Clinical Event Reduction in Acute Coronary Syndrome (TRACER) randomized trial. Eur Heart J. 2017;38:804–810. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Valgimigli M, Bueno H, Byrne RA, et al. 2017 ESC focused update on dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease developed in collaboration with EACTS: The Task Force for dual antiplatelet therapy in coronary artery disease of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and of the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS) Eur Heart J. 2018;39:213–260. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx419. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous