An Investigation of the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Analgesic Effect of Jakyak-Gamcho Decoction: A Network Pharmacology Study
- PMID: 33343676
- PMCID: PMC7732394
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6628641
An Investigation of the Molecular Mechanisms Underlying the Analgesic Effect of Jakyak-Gamcho Decoction: A Network Pharmacology Study
Abstract
Herbal drugs have drawn substantial interest as effective analgesic agents; however, their therapeutic mechanisms remain to be fully understood. To address this question, we performed a network pharmacology study to explore the system-level mechanisms that underlie the analgesic activity of Jakyak-Gamcho decoction (JGd; Shaoyao-Gancao-Tang in Chinese and Shakuyaku-Kanzo-To in Japanese), an herbal prescription consisting of Paeonia lactiflora Pallas and Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fischer. Based on comprehensive information regarding the pharmacological and chemical properties of the herbal constituents of JGd, we identified 57 active chemical compounds and their 70 pain-associated targets. The JGd targets were determined to be involved in the regulation of diverse biological activities as follows: calcium- and cytokine-mediated signalings, calcium ion concentration and homeostasis, cellular behaviors of muscle and neuronal cells, inflammatory response, and response to chemical, cytokine, drug, and oxidative stress. The targets were further enriched in various pain-associated signalings, including the PI3K-Akt, estrogen, ErbB, neurotrophin, neuroactive ligand-receptor interaction, HIF-1, serotonergic synapse, JAK-STAT, and cAMP pathways. Thus, these data provide a systematic basis to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying the analgesic activity of herbal drugs.
Copyright © 2020 Ho-Sung Lee et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
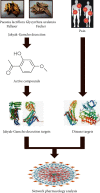


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

