Big Data-Enabled Analysis of DRGs-Based Payment on Stroke Patients in Jiaozuo, China
- PMID: 33343852
- PMCID: PMC7728475
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6690019
Big Data-Enabled Analysis of DRGs-Based Payment on Stroke Patients in Jiaozuo, China
Abstract
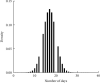
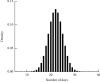
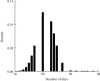
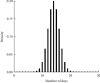
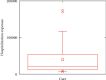
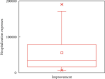
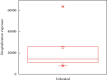
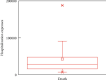
Stroke is the first leading cause of mortality in China with annual 2 million deaths. According to the National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, the annual in-hospital costs for the stroke patients in China reach ¥20.71 billion. Moreover, multivariate stepwise linear regression is a prevalent big data analysis tool employing the statistical significance to determine the explanatory variables. In light of this fact, this paper aims to analyze the pertinent influence factors of diagnosis related groups- (DRGs-) based stroke patients on the in-hospital costs in Jiaozuo city of Henan province, China, to provide the theoretical guidance for medical payment and medical resource allocation in Jiaozuo city of Henan province, China. All medical data records of 3,590 stroke patients were from the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan Polytechnic University between 1 January 2019 and 31 December 2019, which is a Class A tertiary comprehensive hospital in Jiaozuo city. By using the classical statistical and multivariate linear regression analysis of big data related algorithms, this study is conducted to investigate the influence factors of the stroke patients on in-hospital costs, such as age, gender, length of stay (LoS), and outcomes. The essential findings of this paper are shown as follows: (1) age, LoS, and outcomes have significant effects on the in-hospital costs of stroke patients; (2) gender is not a statistically significant influence factor on the in-hospital costs of the stroke patients; (3) DRGs classification of the stroke patients manifests not only a reduced mean LoS but also a peculiar shape of the distribution of LoS.
Copyright © 2020 Dawei Qiao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) Seattle, WA, USA: Technical Reports; 2017. Global trends in disability.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO) Seattle, WA, USA: Technical Reports; 2018. The top 10 causes of death.
-
- Mira K., Andreas L. Global burden of stroke. Seminars in Neurology. 2018;38(2):208–211. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X. 2018. Research on hospitalization costs and case mix of stroke patients of Lanzhou Tertiary Hospital. Master’s thesis.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

