The Effect of Combined Inhalation Aromatherapy with Lemon and Peppermint on Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy: A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 33344211
- PMCID: PMC7737842
- DOI: 10.4103/ijnmr.IJNMR_11_19
The Effect of Combined Inhalation Aromatherapy with Lemon and Peppermint on Nausea and Vomiting of Pregnancy: A Double-Blind, Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
Background: Nausea and vomiting are almost inevitable features of pregnancy which have a serious impact on the quality of life of pregnant women. This study aimed to determine the effects of combined inhalation aromatherapy with lemon and peppermint on nausea and vomiting of pregnancy.
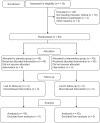
Materials and methods: The parallel randomized clinical trial was conducted on 90 pregnant women suffering from nausea and vomiting of pregnancy referred to health centers in Birjand-Iran- from February 2015 to August 2016. Participants were randomly divided into two groups. The combined lemon and peppermint essential oils were used as an inhaler for the intervention and the placebo for the control group. Both groups were trained to place three drops of the solution onto a cotton ball and keep it in a 3-cm distance of their nose. The intensity of nausea, vomiting and fatigue was assessed through 24-hour Pregnancy Unique Quantization of Emesis (PUQE-24) questionnaire and Fatigue Severity Scale (FSS), respectively.
Results: Mean (SD) scores of nausea and vomiting intensity before the intervention and on the first day of intervention were not significantly different between the two groups, but became significant on the second, third, and fourth days of intervention. The results showed that the effect of time on the mean intensity of nausea and vomiting was significant in the aromatherapy group (F2,84 = 22.92, p < 0.001) but was not significant in the placebo group (F2,78 = 0.26, p = 0.836).
Conclusions: The combined lemon and peppermint aromatherapy could reduce mild to moderate intensity of nausea and vomiting during pregnancy.
Keywords: Aromatherapy; nausea; peppermint; pregnancy.
Copyright: © 2020 Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to declare.
References
-
- Khresheh R. How women manage nausea and vomiting during pregnancy: A Jordanian study. Midwifery. 2011;27:42–5. - PubMed
-
- Matthews A, Haas DM, O'Mathúna DP, Dowswell T, Doyle M. Interventions for nausea and vomiting in early pregnancy. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;3:CD007575. - PubMed
-
- Jarvis S, Nelson-Piercy C. Management of nausea and vomiting in pregnancy. BMJ. 2011;342:1407–12. - PubMed
-
- Lua PL, Zakaria NS. A brief review of current scientific evidence involving aromatherapy use for nausea and vomiting. J Altern Complement Med. 2012;18:534–40. - PubMed
-
- Steel A, Adams J, Sibbritt D, Broom A. The outcomes of complementary and alternative medicine use among pregnant and birthing women: Current trends and future directions. Womens Health. 2015;11:309–23. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous