Treatment of radiation-induced brachial plexopathy with omentoplasty
- PMID: 33344306
- PMCID: PMC7703345
- DOI: 10.4322/acr.2020.202
Treatment of radiation-induced brachial plexopathy with omentoplasty
Abstract
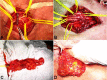
Radiation-induced brachial plexus neuropathy (RIBPN) is a rare and delayed non-traumatic injury to the brachial plexus, which occurs following radiation therapy to the chest wall, neck, and/or axilla in previously treated patients with cancer. The incidence of RIBPN is more common in patients treated for carcinoma of the breast and Hodgkin lymphoma. With the improvement in radiation techniques, the incidence of injury to the brachial plexus following radiotherapy has dramatically reduced. The currently reported incidence is 1.2% in women irradiated for breast cancer. The progression of symptoms is gradual in about two-thirds of cases; the patients may initially present with paresthesia followed by pain, and later progress to motor weakness in the affected limb. We present the case of a 68-year-old female patient with breast cancer submitted to surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy in the year 2000. Eighteen years later, she developed symptoms and signs compatible with RIBPN and was successfully submitted to omentoplasty for pain control. Omentoplasty is an alternative treatment for RIBPN refractory to conservative treatment, which seems to be effective in improving neuropathic pain. However, postoperative worsening of the motor strength is a real possibility, and all candidates for this type of surgery must be informed about the risk of this complication.
Keywords: Brachial Plexus Neuropathies; Neurosurgery; Pain, Intractable; Radiation Injuries.
Copyright: © 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None
Figures
Similar articles
-
Radiation-induced brachial plexus neuropathy: A review.Neurol India. 2019 Jan-Feb;67(Supplement):S47-S52. doi: 10.4103/0028-3886.250704. Neurol India. 2019. PMID: 30688233 Review.
-
Dosimetric analysis of the brachial plexus among patients with breast cancer treated with post-mastectomy radiotherapy to the ipsilateral supraclavicular area: report of 3 cases of radiation-induced brachial plexus neuropathy.Radiat Oncol. 2014 Dec 12;9:292. doi: 10.1186/s13014-014-0292-5. Radiat Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25499205 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Radiation-Induced Brachial Plexopathy.Cureus. 2024 May 10;16(5):e60067. doi: 10.7759/cureus.60067. eCollection 2024 May. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38860104 Free PMC article.
-
Dose--volume modeling of brachial plexus-associated neuropathy after radiation therapy for head-and-neck cancer: findings from a prospective screening protocol.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014 Mar 15;88(4):771-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2013.11.244. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2014. PMID: 24606846
-
The role of surgery in the management of radiation-induced brachial plexopathy: a systematic review.J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2024 Apr;49(4):490-498. doi: 10.1177/17531934231197794. Epub 2023 Sep 8. J Hand Surg Eur Vol. 2024. PMID: 37684017
Cited by
-
Effective Use of Intravenous Lignocaine for Radiotherapy-Induced Brachial Plexopathy.Cureus. 2024 Sep 4;16(9):e68668. doi: 10.7759/cureus.68668. eCollection 2024 Sep. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39371845 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Surgery in the Management of Radiation-Induced Brachial Plexopathy.Hand (N Y). 2024 Nov;19(8):1189-1194. doi: 10.1177/15589447231196902. Epub 2023 Sep 16. Hand (N Y). 2024. PMID: 37715704 Review.

