A Highlight of the Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Blocker Resistance
- PMID: 33344447
- PMCID: PMC7746821
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.580140
A Highlight of the Mechanisms of Immune Checkpoint Blocker Resistance
Abstract
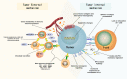
In recent years, as our understanding of tumor immunology is continuously improved, immunotherapy has come to the center stage of cancer therapy and is deemed as the most promising approach for cancer control. Although immunotherapy, particularly immune checkpoint blockade (ICB), has achieved a milestone in several types of tumors, the majority of cancer patients do not benefit from immunotherapy. The dismal outcome of cancer immunotherapy is mainly due to primary or acquired resistance arising from tumor immune evasion. Exploring the mechanisms of tumor immune evasion in the course of immunotherapy may identify biological targets to conquer tumor resistance to immunotherapy. In this review, we highlight tumor cell-intrinsic and -extrinsic factors that may underlie tumor resistance to immune checkpoint blockers. Targeting these factors in combination with immune checkpoint blockers points to the future direction of cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: ICB; PD-1; anti-PD-1; immune microenvironment; immunotherapy resistance.
Copyright © 2020 Huang, Lei, Li, Guo and Liu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Anagnostou V., Smith K., Forde P., Niknafs N., Bhattacharya R., White J., et al. (2017). Evolution of neoantigen landscape during immune checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov. 7 264–276. 10.1158/2159-8290.Cd-16-0828 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

