Gridded Population Maps Informed by Different Built Settlement Products
- PMID: 33344538
- PMCID: PMC7680951
- DOI: 10.3390/data3030033
Gridded Population Maps Informed by Different Built Settlement Products
Abstract
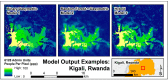
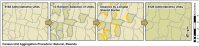
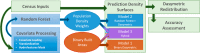
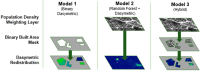
The spatial distribution of humans on the earth is critical knowledge that informs many disciplines and is available in a spatially explicit manner through gridded population techniques. While many approaches exist to produce specialized gridded population maps, little has been done to explore how remotely sensed, built-area datasets might be used to dasymetrically constrain these estimates. This study presents the effectiveness of three different high-resolution built area datasets for producing gridded population estimates through the dasymetric disaggregation of census counts in Haiti, Malawi, Madagascar, Nepal, Rwanda, and Thailand. Modeling techniques include a binary dasymetric redistribution, a random forest with a dasymetric component, and a hybrid of the previous two. The relative merits of these approaches and the data are discussed with regards to studying human populations and related spatially explicit phenomena. Results showed that the accuracy of random forest and hybrid models was comparable in five of six countries.
Keywords: binary dasymetric; built areas; geographic information systems; geography; gridded population distribution; random forest; regression; remote sensing.
© 2018 by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- UN World Population Prospects: The 2017 Revision. Available online: https://www.un.org/development/desa/publications/world-population-prospe... (accessed on 23 April 2018).
-
- UN World Urbanization Prospects: The 2014 Revision. Available online: https://esa.un.org/unpd/wup/ (accessed on 23 April 2018).
-
- Balk D.; Deichmann U.; Yetman G.; Pozzi F.; Hay S.; Nelson A. Determining Global Population Distribution: Methods, Applications and Data. In Advances in Parasitology Global Mapping of Infectious Diseases: Methods, Examples and Emerging Applications; Hay S.I., Graham A.J., Rogers D.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2007; pp. 119–156. ISBN 978-0120317646. - PMC - PubMed
