Effect of FIXed-dose combination of ARb and statin on adherence and risk factor control: The randomized FIXAR study
- PMID: 33346375
- PMCID: PMC9550343
- DOI: 10.5603/CJ.a2020.0167
Effect of FIXed-dose combination of ARb and statin on adherence and risk factor control: The randomized FIXAR study
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of fixed-dose combinations (FDCs) in improving adherence and risk factor control for cardiovascular disease has not been reported consistently. Here, we compared adherence and efficacy between an olmesartan/rosuvastatin FDC and the usual regimen.
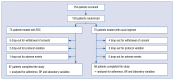
Methods: In this 6-month, open-label, randomized, active-control study, we screened 154 patients; of these, 150 were randomly assigned to receive either olmesartan/rosuvastatin FDC or the usual regimen with separate angiotensin receptor blockers and statins. In total, 135 patients completed the study (median age: 68 years; male: 68.9%). The primary outcome was patients' adherence; the secondary outcomes were changes in blood pressure (BP) and lipid parameters.
Results: During follow-up, adherence in both groups was high and similar between the groups (98.9% and 98.3% in the FDC and usual regimen groups, respectively, p = 0.328). Changes in systolic (-8 and -5 mmHg, respectively, p = 0.084) and diastolic BP (-5 and -2 mmHg, p = 0.092) did not differ significantly, although they were numerically greater in the FDC group. Changes in low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) were greater in the FDC group (-13 and -4 mg/dL, respectively, p = 0.019), whereas changes in other lipid parameters were similar between the groups. The test drugs were well tolerated, showing no difference in safety between the groups.
Conclusions: Patients' adherence was excellent and similar in the groups, whereas the reduction in the LDL-C level was greater in the FDC group. We provide comprehensive information on the adherence and efficacy of an FDC compared to the usual regimen in Korean patients with high cardiovascular risk.
Keywords: drug therapy; hypercholesterolemia; hypertension; renin–angiotensin system; rosuvastatin calcium.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Goff DC, Lloyd-Jones DM, Bennett G, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the assessment of cardiovascular risk: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;129(25):S49–S73. - PubMed
-
- Fihn SD, Gardin JM, Abrams J, et al. 2012 ACCF/AHA/ACP/AATS/PCNA/SCAI/STS guideline for the diagnosis and management of patients with stable ischemic heart disease: executive summary: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association task force on practice guidelines, and the American College of Physicians, American Association for Thoracic Surgery, Preventive Cardiovascular Nurses Association, Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions, and Society of Thoracic Surgeons. Circulation. 2012;126(25):3097–3137. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0b013e3182776f83. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical