Ring finger protein 2 promotes colorectal cancer progression by suppressing early growth response 1
- PMID: 33346749
- PMCID: PMC7803491
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.202396
Ring finger protein 2 promotes colorectal cancer progression by suppressing early growth response 1
Abstract
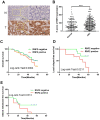
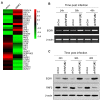
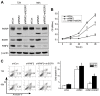
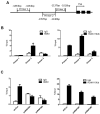
Ring finger protein 2 (RNF2) is an important component of polycomb repressive complex 1. RNF2 is upregulated in many kinds of tumors, and elevated RNF2 expression is associated with a poor prognosis in certain cancers. To assess the function of RNF2 in colorectal cancer, we examined RNF2 protein levels in 313 paired colorectal cancer tissues and adjacent normal tissues. We then analyzed the association of RNF2 expression with the patients' clinicopathologic features and prognoses. RNF2 expression was upregulated in colorectal cancer tissues and was associated with the tumor differentiation status, tumor stage and prognosis. In colorectal cancer cell lines, downregulation of RNF2 inhibited cell proliferation and induced apoptosis. Gene microarray analysis revealed that early growth response 1 (EGR1) was upregulated in RNF2-knockdown cells. Knocking down EGR1 partially reversed the inhibition of cell proliferation and the induction of apoptosis in RNF2-knockdown cells. RNF2 was enriched at the EGR1 promoter, where it mono-ubiquitinated histone H2A, thereby inhibiting EGR1 expression. These results indicate that RNF2 is oncogenic in colorectal cancer and may promote disease progression by inhibiting EGR1 expression. RNF2 is thus a potential prognostic marker and therapeutic target in colorectal cancer.
Keywords: EGR1; RNF2; apoptosis; cell proliferation; colorectal cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Knockdown of RNF2 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells through the upregulation of TXNIP.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 17;8(3):5323-5338. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.14142. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28029659 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosensitization of esophageal carcinoma cells by knockdown of RNF2 expression.Int J Oncol. 2016 May;48(5):1985-96. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3404. Epub 2016 Feb 19. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26936624
-
Knockdown of RNF2 induces apoptosis by regulating MDM2 and p53 stability.Oncogene. 2014 Jan 23;33(4):421-8. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.605. Epub 2013 Jan 14. Oncogene. 2014. PMID: 23318437 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging role of RNF2 in cancer: From bench to bedside.J Cell Physiol. 2021 Aug;236(8):5453-5465. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30260. Epub 2021 Jan 5. J Cell Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33400276 Review.
-
Prognostic role of EGR1 in breast cancer: a systematic review.BMB Rep. 2021 Oct;54(10):497-504. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2021.54.10.087. BMB Rep. 2021. PMID: 34488929 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Unveiling the Intricacies of Monoamine Oxidase-A (MAO-A) Inhibition in Colorectal Cancer: Computational Systems Biology, Expression Patterns, and the Anticancer Therapeutic Potential.ACS Omega. 2024 Aug 9;9(33):35703-35717. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c04100. eCollection 2024 Aug 20. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 39184489 Free PMC article.
-
CNN2 silencing inhibits colorectal cancer development through promoting ubiquitination of EGR1.Life Sci Alliance. 2023 May 15;6(7):e202201639. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202201639. Print 2023 Jul. Life Sci Alliance. 2023. PMID: 37188478 Free PMC article.
-
The epigenetic landscape in intestinal stem cells and its deregulation in colorectal cancer.Stem Cells. 2024 Jun 14;42(6):509-525. doi: 10.1093/stmcls/sxae027. Stem Cells. 2024. PMID: 38597726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification and validation of ubiquitination-related genes for predicting cervical cancer outcome.Front Genet. 2025 Jul 30;16:1578075. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2025.1578075. eCollection 2025. Front Genet. 2025. PMID: 40809844 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and comparison of insulinoma tumor model and pancreatic damage caused by the tumor, and identification of possible markers.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Jan 16;51(1):109. doi: 10.1007/s11033-023-08942-z. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38227104
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

