Reconnaissance of tumor immune microenvironment spatial heterogeneity in metastatic renal cell carcinoma and correlation with immunotherapy response
- PMID: 33346915
- PMCID: PMC7944355
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.13567
Reconnaissance of tumor immune microenvironment spatial heterogeneity in metastatic renal cell carcinoma and correlation with immunotherapy response
Abstract
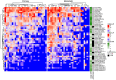
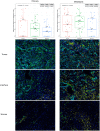
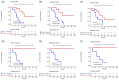
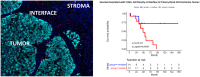
A clearer understanding of the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) in metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) may help to inform precision treatment strategies. We sought to identify clinically meaningful TIME signatures in ccRCC. We studied tumors from 39 patients with metastatic ccRCC using quantitative multiplexed immunofluorescence and relevant immune marker panels. Cell densities were analyzed in three regions of interest (ROIs): tumor core, tumor-stroma interface and stroma. Patients were stratified into low- and high-marker density groups using median values as thresholds. Log-rank and Cox regression analyses while controlling for clinical variables were used to compare survival outcomes to patterns of immune cell distributions. There were significant associations with increased macrophage (CD68+ CD163+ CD206+ ) density and poor outcomes across multiple ROIs in primary and metastatic tumors. In primary tumors, T-bet+ T helper type 1 (Th1) cell density was highest at the tumor-stromal interface (P = 0·0021), and increased co-expression of CD3 and T-bet was associated with improved overall survival (P = 0·015) and survival after immunotherapy (P = 0·014). In metastatic tumor samples, decreased forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3)+ T regulatory cell density correlated with improved survival after immunotherapy (P = 0·016). Increased macrophage markers and decreased Th1 T cell markers within the TIME correlated with poor overall survival and treatment outcomes. Immune markers such as FoxP3 showed consistent levels across the TIME, whereas others, such as T-bet, demonstrated significant variance across the distinct ROIs. These findings suggest that TIME profiling outside the tumor core may identify clinically relevant associations for patients with metastatic ccRCC.
Keywords: T-bet; immune cell markers; immunotherapy; matched pairs; metastatic renal cell carcinoma; tumor immune microenvironment; tumor-associated macrophages.
© 2021 British Society for Immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
The corresponding author certifies that all conflicts of interest, including specific financial interests and relationships and affiliations relevant to the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript (i.e. employment/affiliation, grants or funding, consultancies, honoraria, stock ownership or options, expert testimony, royalties, or patents filed, received or pending), are the following: A. H., A. M. A., L. Z., J. N., J. M. L., J. C., S. Z., S. F., M. F., J. K. T., J. D., S. M., C. M., E. N. K., W. J. S., Y. K. and B. J. M. have no disclosures; P. E. S. is NCCN Bladder and Penile Cancer Panel Member and Vice‐Chair; J. M. is an Associate Center Director at Moffitt Cancer Center, has ownership interest in Fulgent Genetics, Inc., Aleta Biotherapeutics, Inc., Cold Genesys, Inc., Myst Pharma, Inc., and Tailored Therapeutics, Inc. and is a consultant/advisory board member for ONCoPEP, Inc., Cold Genesys, Inc., Morphogenesis, Inc., Mersana Therapeutics, Inc., GammaDelta Therapeutics, Ltd, Myst Pharma, Inc., Tailored Therapeutics, Inc., Verseau Therapeutics, Inc., Iovance Biotherapeutics, Inc., Vault Pharma, Inc., Noble Life Sciences Partners, Fulgent Genetics, Inc., UbiVac, LLC, Vycellix, Inc. and Aleta Biotherapeutics, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Kotecha RR, Motzer RJ, Voss MH. Towards individualized therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 2019; 16:621–33. - PubMed
-
- Cancer Facts & Figures 2019 . 2019. Available at: https://www.cancer.org/cancer/kidney‐cancer/detection‐diagnosis‐staging/... (accessed 3 January 2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

