The role of NO in COVID-19 and potential therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 33347987
- PMCID: PMC7754882
- DOI: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.12.008
The role of NO in COVID-19 and potential therapeutic strategies
Abstract
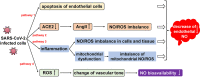
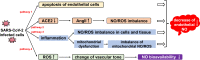
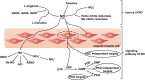
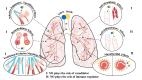
Nitric oxide (NO) is a free radical playing an important pathophysiological role in cardiovascular and immune systems. Recent studies reported that NO levels were significantly lower in patients with COVID-19, which was suggested to be closely related to vascular dysfunction and immune inflammation among them. In this review, we examine the potential role of NO during SARS-CoV-2 infection from the perspective of the unique physical, chemical and biological properties and potential mechanisms of NO in COVID-19, as well as possible therapeutic strategies using inhaled NO. We also discuss the limits of NO treatment, and the future application of this approach in prevention and therapy of COVID-19.
Keywords: Anti-inflammation; Anti-viral; COVID-19; Nitric oxide; Vasodilation.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Marine sulfated polysaccharides as potential antiviral drug candidates to treat Corona Virus disease (COVID-19).Carbohydr Res. 2021 Jul;505:108326. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2021.108326. Epub 2021 May 3. Carbohydr Res. 2021. PMID: 34015720 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Potential Role of Nitric Oxide as a Therapeutic Agent against SARS-CoV-2 Infection.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 5;24(24):17162. doi: 10.3390/ijms242417162. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38138990 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Landscape of Heparin Therapy for COVID-19.Carbohydr Polym. 2021 Feb 15;254:117232. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.117232. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Carbohydr Polym. 2021. PMID: 33357843 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Home pharmacological therapy in early COVID-19 to prevent hospitalization and reduce mortality: Time for a suitable proposal.Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022 Feb;130(2):225-239. doi: 10.1111/bcpt.13690. Epub 2021 Dec 2. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 34811895 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhaled and systemic heparin as a repurposed direct antiviral drug for prevention and treatment of COVID-19.Clin Med (Lond). 2020 Nov;20(6):e218-e221. doi: 10.7861/clinmed.2020-0351. Epub 2020 Aug 30. Clin Med (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32863274 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Nitric Oxide and its Derivatives Containing Nasal Spray and Inhalation Therapy for the Treatment of COVID-19.Curr Pharm Des. 2022;28(46):3658-3670. doi: 10.2174/1381612829666221024124848. Curr Pharm Des. 2022. PMID: 36284382 Review.
-
The Molecular Basis of COVID-19 Pathogenesis, Conventional and Nanomedicine Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 21;22(11):5438. doi: 10.3390/ijms22115438. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34064039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Melatonin interferes with COVID-19 at several distinct ROS-related steps.J Inorg Biochem. 2021 Oct;223:111546. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2021.111546. Epub 2021 Jul 17. J Inorg Biochem. 2021. PMID: 34304092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heparin prevents in vitro glycocalyx shedding induced by plasma from COVID-19 patients.Life Sci. 2021 Jul 1;276:119376. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119376. Epub 2021 Mar 27. Life Sci. 2021. PMID: 33781826 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Mechanisms for Organoprotective Effects of Exogenous Nitric Oxide in an Experimental Study.Biomedicines. 2024 Mar 23;12(4):719. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040719. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672075 Free PMC article.
References
-
- 2020.12.01. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

